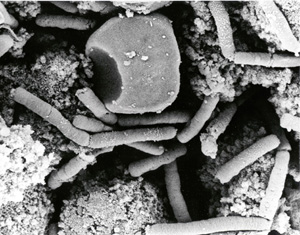
Anthrax, once upon a time, was a marginal disease in people, afflicting sheepshearers and few others. Most people who contracted it at all got the cutaneous form of the disease, which forms black scabs on the skin that look like anthracite coal (hence the name "anthrax"). But in autumn 2001, around the time of the terrorist attacks on New York and Washington, deadly anthrax spores began to be spread in letters mailed to news organizations and prominent government officials. Several people inhaled the spores and died from the much more deadly pulmonary form of the disease. Fear of the anthrax contagion was rampant. The very idea that small quantities of white powder in envelopes could be anthrax spores has changed Post office practices to such a degree that they have adversely affected many citizens' daily routines, including my own.
Anthrax spores became infamous as a potential weapon during the Second World War, when the British test-fired anthrax bombs on the Scottish island of Gruinard. The bacterium's infectious spores spread across the island's 520 acres and left Gruinard uninhabitable for nearly fifty years. Not until the late 1980s was the island decontaminated. The cleanup required four years of effort by a large crew; wielding almost 300 tons of formaldehyde--a sobering testament to the durability, both temporal and chemical, of anthrax spores.
What is still unknown, even after the island's cleanup, is the bacterium's ecology. Is anthrax just a kind of bacterial sit-and-wait predator, which bides its time until a sheepshearer cuts himself or a letter handler inhales a cloud of spore-laden dust? The anthrax bacterium is readily grown in laboratory culture. But where is it in nature?
Our eclectic reading habits have helped my students and me disentangle one strand of the anthrax story. We recently discovered that a common laboratory bacterium, identical in all but the most trifling ways with the organism that causes anthrax, lives deep inside the intestines of many healthy animals. But the scientific story of anthrax does not begin with our work, or with the terrorist attacks of 2001, or even with the episode on Gruinard. It begins in the field, on the ties of railroad tracks in the part of New Jersey that borders Pennsylvania, in middle of the nineteenth century. The central figure of the story is a Philadelphia naturalist named Joseph Leidy, once famous but now largely forgotten. Leidy was the first to observe our laboratory bacterium in its natural habitat, living in the intestines of animals.
Leidy's scientific legacy affects everyone, yet he enjoys almost no posthumous reputation. A nineteenth-century polymath, who was initially trained as a physician, Leidy became one of his era's greatest naturalists. He identified the nematode in undercooked pork that is responsible for trichinosis, a debilitating and sometimes deadly muscle disease. He described and named some 400 new species of North American animals, plants, and mushrooms and other fungi. He was the father of modern vertebrate paleontology in North America. He properly interpreted certain fossil remains found in the West as belonging to dinosaurs. Leidy worked tirelessly on the reconstruction of the history of the Earth's surface by investigating metamorphic rocks and eroded minerals. He even discovered a thriving diversity of microscopic life adhering to fish scales, after he had admonished his fishmonger in the Philadelphia open market to neither damage nor remove them.
Exceedingly broad in his choices of nature's gifts to investigate, Leidy published some 400 scientific papers during a fifty-year career. All the papers are single-authored--not because he was uncooperative (there is much evidence of his generosity toward his scientific colleagues as well as his students), but because he was consistently ahead of his colleagues. As Leonard Warren makes clear in his recent biography, Joseph Leidy: The Last Man Who Knew Everything, the main reason the history of science overlooks his accomplishments relates to the breadth of his interests. Leidy's science could never be assigned to a single discipline. Yet his writings never generalize. Leidy stays so close to his own data that to those today who are looking to the past for overarching theories or general principles, he seems to deal only with trivia.
Today's neglect, however, contrasts sharply with the fame he achieved during his lifetime as a scientist, particularly in his native Philadelphia. A larger-than-life statue of him stands outside the city's Academy of Natural Sciences, and the building housing the biology department at the University of Pennsylvania bears his name. Several mountains in the western United States are also named for him. And he helped President Lincoln found the National Academy of Sciences.
In spite of Leidy's wide-ranging interests and activities, he was never away from his first scientific passion for long: the study of the microcosm. Warren conveys Leidy's boundless curiosity for the microworld by quoting a characteristic remark: "How can life be tiresome," Leidy asked, "so long as there is still a new rhizopod [amoeba] undescribed?" Leidy certainly never tired. The archives of the Academy of Natural Sciences in Philadelphia hold the delicate, accurate, even lovingly rendered drawings of the microcosm that he made throughout his career.
One of Leidy's pleasures was to take long walks across the Delaware River from Philadelphia to New Jersey, where he would explore what were then isolated and bucolic landscapes along the railroad tracks. Next to the rail beds, Leidy observed with customary curiosity, were discarded ties beset with "white ants," as termites were then called. By contrast, he noted, in sound and sturdy ties the insects were seldom present. Leidy long wondered what the insects ate, because termites also occurred so often in teeming numbers in rotting logs and fences, where no obvious sources of food were present.
Leidy punctured the guts of the insects and examined the contents under his microscope. Amid liquid brown matter in the hindgut, he found the pieces of wood the insects had eaten. But his greatest astonishment came when he looked closely at the brown liquid: "fit was] swarming with myriads of parasites ... wonderful in number, variety, and form." Watching this scene under the microscope, he later wrote, reminded him of "the turning out of a multitude of persons from the door of a crowded meeting-house."
The episode came to be one of Leidy's most abiding microbial discoveries. The myriad citizens in Leidy's jostling crowds turned out to be symbionts that are omnipresent in healthy termites. Leidy later discovered similar microorganisms in wood-eating cockroaches. In 1850 he introduced those intestinal inhabitants to the world of science, in a paper titled "On the existence of entophyta in healthy animals as a natural condition." Among the "entophyta" (literally "plants [living] inside") that Leidy discovered in the termite was a bacterium that, more than a century later, became the subject of our study.
A large teaching chart, completed by Leidy in 1888, shows the life-forms within the intestine of Julus marginatus, a millipede; the arthropod plays host, as Leidy by then had realized, to some of the same microorganisms as the New Jersey termites do [see illustration on preceding page]. In fact, as he recorded on the chart, he discovered bundles of long filaments, which he dubbed "jointed threads," in the intestines of a number of arthropods.
Leidy went on to depict and describe the development and propagation of shiny spherical bodies, or spores, along many of the filaments. He noted that mature spores are released into the digestive tract, and he suspected that from there they move through the intestines by peristalsis. It is now known that they are defecated into the soil, where they survive because of their high resistance to desiccation and heat.
But though the spores from the cells that make up Leidy's jointed threads spend part of their life history in the soil, it is not useful to describe them as soil bacteria, because they do not grow in soil. To reach the next stage in their life cycle, they must be carried, ingested, or blown into some wet environment abundant with food: a clump of decaying vegetation in a farm pond, perhaps, or the intestine of another animal, or a petri dish of nutrient agar in a laboratory. If the spores reach such nutritious surroundings, they germinate; then, seizing the day, they grow and multiply quickly for as long as they are surrounded by enough air, food, and water to continue.
Leidy recognized from the outset that the spores of jointed-thread entophytes that occur in healthy organisms might be related to contagion. As he observed,
Contagious diseases and some others might have their origin and reproductive character through the agency of cryptogamic spores, which from their minuteness and lightness are so easily conveyed from place to place through the atmosphere by means of the gentlest zephyr.
The word cryptogamic (from the Greek crypto-, "hidden," plus 2amein, "to marry") in Leidy's time referred to an archaic grouping of seedless plants (such as ferns and mosses), as well as to algae and bacteria (regarded as plants that lack flowers). Only two great groups, or "kingdoms," of living beings were recognized. If an organism was not an animal, it had to be a plant.
Given that dichotomous classification, it should be no surprise that Leidy described his jointed threads in the language of botany. The organisms tended to be "rooted" to the epithelium, or inside surface layer of cells, of the animal's intestine. Less frequently, they were rooted to one of the other intestinal inhabitants. They did not swim. They developed shiny spheres that he suspected were "plant spores." Clearly, then, the jointed thread was a plant. (Such a classification does not mean that Leidy failed to recognize his jointed threads as bacteria. It was just that they--and for that matter, all bacteria--were clearly not animals, and so they had to be plants.)
From various termite species, Leidy identified a series of related but distinguishable jointed threads, which he named Arthromitus cristatus. He classified the jointed threads from the common cockroach as a second species, A. intestinalis. After Leidy's detailed scientific articles and drawings were published, such jointed threads were also discovered in the intestines of many other animals, including ducks and dogs. Jointed threads, it turns out, are "plants" inside intestines everywhere.
A century and a half after Leidy, my colleagues and I have often followed in his footsteps in our studies of the microbial communities in termites, wood-eating cockroaches, and a few other anthropods. On occasion, I have collected termites in Arizona south of Tucson, and was fortunate to examine what lives inside the Sonoran desert termite (Pterotermes occidentis). We keep termites in the laboratory, and we have often observed, with variations, just what Leidy depicted in his illustrations. We have even seen the same branching filaments that Leidy drew but did not name.
We were not the first, however, to reconfirm Leidy's findings. In the 1940s, the protozoologist Harold Kirby prepared beautiful, permanent stained slides for the microscopic study of symbionts in the guts of termites. Kirby's interest was in wood nymphs--protists that lack mitochondria, swim vigorously, and digest hefty wood fragments--but his slides include the same straight and branched Arthromitus-like filaments that Leidy's drawings portray. Sixty years after Kirby, we, too, saw the filaments.
One nontermite host of Arthromitus that my colleagues and I examined in depth was the common sow bug, Porcellio scaber. Sow bugs form hordes in the warm, smelly monkey house where golden lion tamarins (Leontopithecus rosalia), native to Brazil, live at the EcoTarium in Worcester, Massachusetts. The sow bugs love to feed and breed under rocks and in other dark crannies where the monkeys scamper in that steamy enclosure. Jeremy Jorgensen, then a graduate student at the University of Massachusetts-Amherst, isolated Arthromitus from the sow bugs' intestines with ease. Jorgensen's simple but effective method of isolating the spores was simply to boil the intestinal contents of sow bugs continuously for at least twenty minutes. Among all the other intestinal bacteria, only Arthromitus spores survived the boiling.
Jorgensen also found Arthromitus filaments in the intestines of the tamarins. He figured out how the bacteria got there when he saw the sow bugs crawling over the tamarins' food and defecating on it with abandon. The cycle of Arthromitus propagation was not complete, however. How did the bacteria get into the sow bugs? Jorgensen, learning from the keeper of the monkey house that the noisy little primates simply did not produce feces any time after 8 A.M., visited the monkey house at dawn. Promptly as the sun rose, all the tamarins--with surprising synchronicity--dropped their feces at once. Jorgensen watched in amazement as sow bugs, thousands of them, emerged as one from their hiding places to ingest the tamarin poop almost instantly. Here was the completion of the life cycle: the "soil" bacteria enter the intestines of the insects and the mammals by the same route--their mouths.
Meanwhile, our work with the Arthromitus bacterium that occurs in termites continued. With the help of Frederick A. Rainey, a microbiologist at Louisiana State University in Baton Rouge, we sequenced the gene for the bacterium's ribosomal RNA, and compared the sequences with other published ones. We measured many bacterial traits of Arthromitus, and we studied it with the electron microscope. Those data, along with the ribosomal RNA sequence, confirmed that Arthromitus is equivalent to a large, familiar, rod-shaped bacterium that is easily grown in the microbiologist's laboratory: a harmless spore-forming microorganism known as Bacillus cereus.
Recognizing that Bacillus cereus is Arthromitus may be of interest to microbiologists, but the interest these days transcends the boundaries of the field. The genus Bacillus includes the anthrax bacterium, B. anthracis. No one had realized that Bacillus, the organism so commonly cultured and often considered a pest or contaminant in the laboratory, is essentially the same organism to which Leidy had given the name Arthromitus in the wild. The rod-shaped bacteria cultured on an agar petri dish look quite different from the shiny spores and the cells that make up "jointed threads" in their native habitat--the digestive systems of healthy animals. Leidy's work on Arthromitus is not so well known today, but modern science, and the rest of us, ignore it at our peril.
Part of the difficulty in making this connection, oddly enough, arose from the fact that, since 1980, practices with laboratory bacteria have bee codified. The professional microbiologist may not describe and name a bacterium simply because it appears in nature--say, within an animal, on a plant or mushroom, or as a coating of hundreds on wood-nymph protists. According to the international rules of bacterial nomenclature, a microorganism must be described and named only in "pure culture" In other words, the microorganism must be described as it lives and grows in a test tube, all by itself. Furthermore, two different pure-culture samples of bacteria must be banked in at least two different international culture collections.
The irony of those rules is that several features of the bacteria in the wild--their habit of assembling into filaments; their shorter, swimming filaments that pursue a docking site on the lining of the animal's intestine; and the spore-attachment fibers [see image on preceding page]--tend not to form outside an animal's intestine. Those accoutrements of symbiotic life are dispensable, and dispensed with, under laboratory conditions, as Arthromitus, the jointed thread that lives "in healthy animals as a natural condition," becomes Bacillus, the test-tube bacterium in the service of microbiology.
The causative agent of anthrax, B. anthracis, differs from B. cereus (and, equivalently, test-tube Arthromitus) in one crucial respect: B. anthracis is armed. B. anthracis is B. cereus with two or three additional plasmids: lengths of DNA formed into tight rings. The relation of B. cereus to B. anthracis is similar to that between a Homo sapiens by himself and a Homo sapiens with an inherited gun. Like the gun, the plasmids may be passed from parent to offspring. Their ammunition is simply the genes that code for a terrible toxin and for a coating that protects the bacterium carrying the toxin from the host's immune system.
David J. Ellar of the University of Cambridge is an expert on the huge genus Bacillus. In addition to B. cereus and B. anthracis, many other members of the genus exist: oxygen-breathing, heat-resistant spore-formers. A large number of those walled, rod-shaped bacteria regularly associate with insects, mammals, or agricultural plants. Ellar heads a Bacillus genome project intent on obtaining a full sequence of bacilli other than B. anthracis to compare with that dangerous one.
After my student colleagues, including Jorgensen, Michael Dolan, Rita Kolchinsky, and Andrew Wier, identified Arthromitus with Bacillus, Ellar asked me to provide him with a sample of Arthromitus newly isolated from an insect intestine. He wanted to examine the genome of a bacillus that had never been tamed by laboratory life. Unfortunately, a lack of research funding and other assistance made it impossible to oblige him, but we had a lively conversation. Ellar remembered once observing a culture of bacilli that had just been acquired for his collection. Examining the culture through a microscope, he had been perplexed by the little fibers he had seen growing on the spores. After he read our Arthromitus papers, Ellar realized that in one new culture the spores had retained their attachment fibers, typical of wild Arthromitus. The culture probably had not been in the laboratory for long. I asked him where he had found the new strain. He looked through his extensive records and called back excitedly a few weeks later. The bacillus with the tiny fibers had been collected in the Pasoh forest of Malaysia. And yes, it came from a termite mound.
Leidy's meticulous observation of live organisms, Kirby's equally keen empiricism, and our comparative work have made it clear that Bacillus anthracis, the anthrax culprit, comes from a long line of symbionts in animal intestines. Those symbionts are filaments that live inside people, sheep, and various members of barnyard and wild animal communities. Without its two extra plasmids, the bacterium is harmless. It grows on mushy food both inside and outside the intestine. And when conditions deteriorate, it forms remarkably tolerant propagules--tough, even boilproof, shiny, spores by the millions that waft on air. If we are to be afraid of anthrax, as indeed we must be, we need to condemn those who would deliberately culture a bacillus that is armed with the dangerous plasmids that enable it to be a pathogen, a freak of nature, rather than a law-abiding citizen of the intestinal microcosm.
COPYRIGHT 2005 Natural History Magazine, Inc.
COPYRIGHT 2005 Gale Group