Herpes zoster
Herpes zoster, colloquially known as shingles, is the reactivation of varicella zoster virus, leading to a crop of painful blisters over the area of a dermatome. It occurs very rarely in children and adults, but its incidence is high in the elderly (over 60), as well as in any age group of immunocompromised patients. It affects some 500,000 people per year in the United States. Treatment is generally with antiviral drugs such as acyclovir. Many patients develop a painful condition called postherpetic neuralgia which is often difficult to manage. more...
In some patients, herpes zoster can reactivate subclinically with pain in a dermatomal distribution without rash. This condition is known as zoster sine herpete and may be more complicated, affecting multiple levels of the nervous system and causing multiple cranial neuropathies, polyneuritis, myelitis, or aseptic meningitis.
The word herpes came from Greek, which is cognate with serpent and, as can be expected, herpetology. Interestingly, the skin disease is also commonly known as "snake" in Chinese.
Signs and symptoms
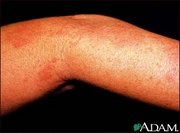
Often, pain is the first symptom. This pain can be characterized as stinging, tingling, numbing, or throbbing, and can be pronounced with quick stabs of intensity. Then 2-3 crops of red lesions develop, which gradually turn into small blisters filled with serous fluid. A general feeling of unwellness often occurs.
As long as the blisters have not dried out, HZ patients may transmit the virus to others. This could lead to chickenpox in people (mainly young children) who are not yet immune to this virus.
Shingles blisters are unusual in that they only appear on one side of the body. That is because the chickenpox virus can remain dormant for decades, and does so inside the spinal column or a nerve fiber. If it reactivates as shingles, it affects only a single nerve fiber, or ganglion, which can radiate to only one side of the body. The blisters therefore only affect one area of the body and do not cross the midline. They are most common on the torso, but can also appear on the face (where they are potentially hazardous to vision) or other parts of the body.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis is visual — very few other diseases mimic herpes zoster. In case of doubt, fluid from a blister may be analysed in a medical laboratory.
Pathophysiology
The causative agent for herpes zoster is varicella zoster virus (VZV). Most people are infected with this virus as a child, as it causes chickenpox. The body eliminates the virus from the system, but it remains dormant in the ganglia adjacent to the spinal cord or the ganglion semilunare (ganglion Gasseri) in the cranial base.
Generally, the immune system suppresses reactivation of the virus. In the elderly, whose immune response generally tends to deteriorate, as well as in those patients whose immune system is being suppressed, this process fails. (Some researchers speculate that sunburn and other, unrelated stresses that can affect the immune system may also lead to viral reactivation.) The virus starts replicating in the nerve cells, and newly formed viruses are carried down the axons to the area of skin served by that ganglion (a dermatome). Here, the virus causes local inflammation in the skin, with the formation of blisters.
Read more at Wikipedia.org