The bone-marrow oedema syndrome is associated with local vascular disturbances and may be
treated either conservatively or by core decompression after which recovery may take several weeks. We describe a 15-year-old girl with bone-marrow oedema of the left acetabulum which was confirmed by MRI. She presented with a four-week history of severe constant pain. Routine blood tests and plain radiographs were normal. She was treated with intravenous infusions of iloprost on five consecutive days (20 (mu)g administered in 500 ml of sodium chloride). Iloprost causes vasodilatation with reduction of capillary permeability and it inhibits platelet aggregation. She had relief from pain at rest after three days of treatment and was completely free from symptoms after two weeks. MRI after six weeks showed almost complete resolution of the marrow oedema and was normal after four months. This is the first report of the pharmacological treatment of the bone-marrow oedema syndrome in children.
J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 2002;84-B: 1050-2.
Received 17 January 2002; Accepted after revision 19 March 2002
The bone-marrow oedema syndrome of the hip is a rare cause of acute pain in children. Cases affecting the femoral head have been described. 1,2 It is also called transient osteoporosis and may be a reversible early stage of avascular necrosis, 3-7 a distinct self-limiting transient condition8,9 or a form of reflex sympathetic dystrophy.10
Bone-marrow oedema in juveniles has been reported as an early finding in patients with osteomyelitis11 or Perthes' disease.12
It resolves with conservative treatment but resolution can take up to 12 months 1,2,4,8,13 Although treatment by core decompression may resolve the symptoms more quickly, invasive treatment should be offered to young patients with caution.4,14-17
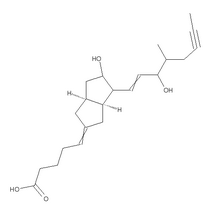
We report a young patient suffering from bone-marrow oedema in the acetabulum which was diagnosed by MRI. We have previously described excellent results after the use of iloprost, a stable prostacyclin analogue, for the treatment of bone-marrow oedema of the talus.17 It induces vasodilatation with reduction of capillary permeability and inhibits platelet aggregation.18 This is the first form of treatment which addresses the vascular abnormalities, which are the probable cause of this condition.
Case report
A 15-year-old girl presented with a four-week history of severe constant pain in the left hip. The range of movement was normal with pain felt in the groin at the limit of flexion. An initial radiograph of the left hip and routine blood tests were normal. MRI showed a characteristic low-intensity signal in T1-weighted (Fig. 1a) and an increased signal in T2-weighted sequences (Fig. lb) indicating marrow oedema in the acetabulum. There was a small effusion in the hip. The proximal femur was normal, as was the right hip.
She was treated by a series of five infusions of 20 jIg of iloprost (Ilomedin; Schering AG, Germany) on five consecutive days. It was administered in 500 ml of sodium chloride solution over periods of between five and 11 hours. She reported a slight headache during the first infusion. There was no alteration in either blood pressure or pulse rate during the infusion. There was relief from pain at rest after the first three days of treatment and from pain on activity within two weeks. MRI after six weeks showed almost complete resolution of the marrow oedema which only persisted in the posterior aspect of the acetabulum (Fig. 1c). A final MRI after three months showed normal signal patterns in the T1- and T2-weighted images (Figs Ic and ld). Six months after treatment she remained free from symptoms with no limitation of daily or. sporting activities.
Discussion
To our knowledge bone-marrow oedema of the acetabulum in a young patient has not been previously reported. Hoffmann 19 described two cases affecting the acetabulum in adults, one secondary to dysplasia and one to osteoarthritis. The success of different forms of treatment is dependent on the stage of the disease. Good results can be obtained but the prognosis is poorer with advanced bone necrosis.20 Thus, early diagnosis and rapid and effective treatment are essential. The options for treatment, however, are limited. Conservative management has been recommended, in particular in the rare cases of bone-marrow oedema in children, 1,2 consisting of symptomatic therapy and reduction of weight-bearing until clinical and radiological resolution. Although this is safe and can give good results it may take a long time.13 Other authors report good results after core decompression ,3,4,14-16 based on the theory that the pain is due to an elevated intramedullary pressure. Core decompression can lead to rapid and complete relief from symptoms and resolution of the changes seen on MRI. Although these authors have reported a low rate of complications such as femoral fracture, additional measures such as six weeks of partial or non-weight-bearing and physiotherapy are usually required.
Our aim was to address the causative vascular abnormalities by using the vasoactive compound iloprost. It is a stable prostacyclin analogue which is used in the treatment of critical ischaemia as a result of peripheral vascular disease or diabetic angiopathy. Its effects on the terminal vascular bed include vasodilatation, reduction of capillary permeability and inhibition of platelet aggregation. It also has an effect on the concentrations of endothelin, oxygen radicals and leukotrienes, and inhibits lipid peroxidation.18,21 The most frequent side-effects of treatment with iloprost are headache, nausea and flushes. Contraindications include pregnancy, anticoagulation treatment, cardiac failure, recent myocardial infarction, unstable angina pectoris or peptic ulcer.
Iloprost has been successfully used in more than 300 patients in our department since 1998. They had bonemarrow oedema or early avascular necrosis at various sites, including the femoral head, the femoral condyles, the tibia, the hand, the metatarsal bones and the talus.17
Bone-marrow oedema is rare in children and since this is the first reported case of involvement of only the acetabulum, comparison with other possible forms of treatments is not possible. The rapid resolution of symptoms and regression of the MRI changes confirm the place of iloprost in the treatment of this condition in young patients.
One or more of the authors have received or will receive benefits for personal or professional use from a commercial party related directly or indirectly to the subject of the article.
References
1. Nicol RO, Williams PF, Hill DJ. Transient osteopaenia of the hip in children. J Pediatr Orthop 1984;4:590-2.
2. Pay NT, Singer WS, Bartal E. Hip pain in three children accompanied by transient abnormal findings on MR images. Radiology 1989;171:147-9.
3. Hofmann S, Engel A, Neuhold A, et al. Bone-marrow oedema syndrome and transient osteoporosis of the hip: an MRI-controlled study of treatment by core decompression. J Bone Joint Surg [BrI 1993;75-B:210-6.
4. Hofmann S, Schneider W, Breitenseher M, Urban M, Plenk H, Jr. "Transient osteoporosis" as a special reversible form of femur head necrosis. Orthopade 2000;29:411-9.
5. Neuhold A, Hofmann S, Engel A, et al. Bone marrow edema of the hip: MR findings after core decompression. J Comput Assist Tomogr 1992;16:951-5.
6. Plenk H, Jr., Hofmann S, Eschberger J, et al. Histomorphology and bone morphometry of the bone marrow edema syndrome of the hip. Clin Orthop 1997;334:73-84.
7. Vande Berg BE, Malghem JJ, Labaisse MA, Noel HM, Maldague BE. MR imaging of avascular necrosis and transient marrow edema of the femoral head. RadioGraphics 1993;13:501-20.
8. Gallant GG, Fisher RL, Sziklas JJ. Transient regional osteoporosis of the ankle and foot: a report of four cases and review of the literature. Orthop Rev 1994;23:405-9.
9. Kim YM, Oh HC, Kim HF. The pattern of bone marrow oedema on MRI in osteonecrosis of the femoral head. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 2000;82-B:837-41.
10. Doury P. Bone-marrow oedema, transient osteoporosis, and algodystrophy. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 1994;76:993-4.
11. Hauer MP, Uhl M, Allmann KH, et al. Comparison of turbo inversion recovery magnitude (TIRM) with T2-weighted turbo spinecho and TI-weighted spin-echo MR imaging in the early diagnosis of acute osteomyelitis in children. Pediatr Radiol 1998;28:846-50.
12. Atsumi T, Kuroki Y. Role of impairment of blood supply of the femoral head in the pathogenesis of idiopathic osteonecrosis. Clin Orthop 1992;277:22-30.
13. Froberg PK, Braunstein EM, Buckwalter KA. Osteonecrosis, transient osteoporosis, and transient bone marrow edema: current concepts. Radiol Clin North Am 1996;34:273-91.
14. Hofmann S, Engel A, Schneider W. The histomorphological substrate in bone marrow edema syndrome (BMES) of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 1997;79, Suppl. 11:216.
15. Leder K, Knahr K. Effect of core decompression in the early stages of necrosis of the femoral head. Orthop Int 1995;3:411-22.
16. Mont MA, Schon LC, Hungerford MW, Hungerford DS. Avascular necrosis of the talus treated by core decompression. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 1996;78-B:827-30.
17. Aigner N, Petje G, Steinboeck G, et al. Treatment of bone-marrow oedema of the talus with the prostacyclin analogue iloprost: an MRIcontrolled investigation of a new method. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 2001;83-B:855-8.
18. Grant SM, Goa KL. Iloprost: a review of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties, and therapeutic potential in peripheral vascular disease, myocardial ischaemia and extracorporeal circulation procedures. Drugs 1992;43:889-924.
19. Hofmann S. Bone marrow oedema in transient osteoporosis, reflex sympathetic dystrophy and osteonecrosis. In: Jacob RP, Fulford P, Horan F, eds. European Instructional Course Lectures. London. The British Editorial Society of Bone and Joint Surgery 1999:138-51.
20. Schneider W, Breitenseher M, Engel A, et al. The value of core decompression in treatment of femur head necrosis. Orthopade 2000;29:420-9.
21. Erlansson M, Svensjo E, Bergqvist D. Leukotriene 134-induced permeability increase in postcapillary venules and its inhibition by three different antiinflammatory drugs. Inflammation 1989;13:693-705.
N. Aigner, G. Petje, W. Schneider, C. Krasny, F. Grill, F. Landsiedl
From the Orthopaedic Hospital Vienna-Speising, Vienna, Austria
N. Aigner, MD, Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon
G. Petje. MD, Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon
W. Schneider, MD. Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon
C. Krasny, MD, Resident
F. Grill, MD, Head of Department
F. Landsiedl, MD, Head of Department
First, Second and Paediatric Orthopaedic Departments, Orthopaedic Hospital Vienna-Spei sing, Speisinger Strasse 109, A-1130 Vienna, Austria.
Correspondence should be sent to Dr N. Aigner.
Copyright British Editorial Society of Bone & Joint Surgery Sep 2002
Provided by ProQuest Information and Learning Company. All rights Reserved