LAS VEGAS - Pulling itself out of the mess caused by rampant fraud and abuse by providers in past years, the lymphedema and vascular disease industry is looking to pass legislation that would require coverage for the care and therapy of these diseases.
Cindy Ortiz, owner of Nevada Vascular and Lymphatic Specialty Company, has devoted nearly two years to working with the National Lymphedema Network (NLN) on legislation, which is framed as patient's rights legislation with a focus on long-term disease management.
"You either have to treat the disease or treat the complications," said Ortiz.
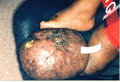
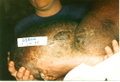
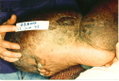
Complications of lymphedema include chronic wounds, cellulitis, immobility and amputation. Treatment of these problems cost both Medicare and other payers $8.8 billion a year, said Ortiz.
"Each person's condition is so different. That is why we need the policy makers on our side," said Saskia Thiadens, executive director and founder of the NLN. "Untreated, the lymphedema will only get worse, and the treatment will only get more expensive."
Ortiz and the NLN's goal is to pass legislation requiring Medicare and other payers to pay for treatment of lymphedema, including compression hosiery and lymphedema pumps.
"The physician needs to determine the treatment and length of treatment, not the insurance companies," said Thiadens.
The legislative process gained a major victory last year with the passing of legislation in Virginia. The bill, which took effect Jan. 1, said that each insurer in the state must provide coverage for lymphedema, including equipment, supplies and outpatient self-management training. Legislation is being considered in Massachusetts and New York, said Thiadens.
Medicare stopped paying on the lymphedema pump after fraud and abuse overran the code. That is why Ortiz said she is also looking for stricter guidelines and qualifications for providers in the field.
By JENNIFER GUNDERSEN, ASSOCIATE EDITOR
Copyright United Publications, Inc. Feb 2004
Provided by ProQuest Information and Learning Company. All rights Reserved