Spinal cord injury
Spinal cord injury, or myelopathy, is a disturbance of the spinal cord that results in loss of sensation and mobility. The two common types of spinal cord injury are: more...
- Trauma : automobile accidents, falls, gunshots, diving accidents, etc.
- Disease : polio, spina bifida, tumors, Friedreich's ataxia, etc.
It is important to note that the spinal cord does not have to be completely severed for there to be a loss of function. In fact, the spinal cord remains intact in most cases of spinal cord injury.
Spinal cord injuries are not the same as back injuries such as ruptured disks, spinal stenosis or pinched nerves. It is possible to "break one's neck or back" and not sustain a spinal cord injury if only the vertebrae are damaged, but the spinal cord remains intact.
About 450,000 people in the United States live with spinal cord injury, and there are about 11,000 new spinal cord injuries every year. The majority of them (78%) involve males between the ages of 16-30 and result from motor vehicle accidents (42%), violence (24%), or falls (22%).
The Effects of Spinal Cord Injury
The exact effects of a spinal cord injury vary according to the type and level injury, and can be organized into two types:
- In a complete injury, there is no function below the level of the injury. Voluntary movement is impossible and physical sensation is impossible. Complete injuries are always bilateral, that is, both sides of the body are affected equally.
- A person with an incomplete injury retains some sensation below the level of the injury. Incomplete injuries are variable, and a person with such an injury may be able to move one limb more than another, may be able to feel parts of the body that cannot be moved, or may have more functioning on one side of the body than the other.
In addition to a loss of sensation and motor function below the point of injury, individuals with spinal cord injuries will often experience other changes.
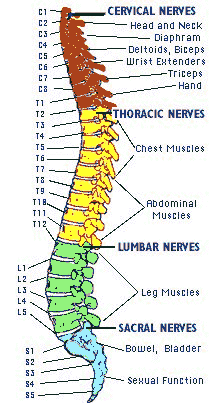
Bowel and bladder function is associated with the sacral region of the spine, so it is very common to experience dysfunction of the bowel and bladder. Sexual function is also associated with the sacral region, and is also affected very often. Injuries very high on the spinal cord (C-1, C-2) will often result in a loss of many involuntary functions, such as breathing, necessitating mechanical ventilators or diaphragmatic pacemakers. Other effects of spinal cord injury can include an inability to regulate heart rate (and therefore blood pressure), reduced control of body temperature, inability to sweat below the level of injury, and chronic pain.
The Location of the Injury
Knowing the exact level of the injury on the spinal cord is important when predicting what parts of the body might be affected by paralysis and loss of function.
Read more at Wikipedia.org