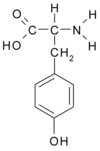
Tyrosine
Tyrosine (from the Greek tyros, meaning "cheese", as it was first discovered in cheese), 4-hydroxyphenylalanine, or 2-amino-3(4-hydroxyphenyl)-propanoic acid, is one of the 20 amino acids that are used by cells to synthesize proteins. It has a phenol side chain. more...
Tyrosine is converted to DOPA by Tyrosine hydroxylase, an enzyme.
It plays a key role in signal transduction, since it can be tagged (phosphorylated) with a phosphate group by protein kinases to alter the functionality and activity of certain enzymes. (In its phosphorylated state, it is sometimes referred to as phosphotyrosine.) Other important biological functions of tyrosine are as a precursor of the thyroid hormone, thyroxine, the pigment, melanin and of the biologically active catecholamines (e.g., dopamine, noradrenaline and adrenaline).
In Papaver somniferum, the opium poppy, it is used to produce morphine.
Biosynthesis
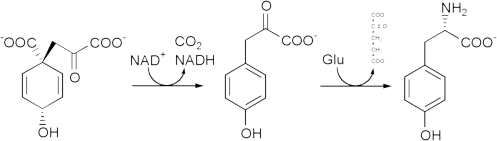
Tyrosine cannot be completely synthesized by animals, although it can be made by hydroxylation of phenylalanine if the latter is in abundant supply. It is produced by plants and most microorganisms from prephenate, an intermediate on the shikimate pathway.
Prephenate is oxidatively decarboxylated with retention of the hydroxyl group to give p-hydroxyphenylpyruvate. This is transaminated using glutamate as the nitrogen source to give tyrosine and α-ketoglutarate.
 is the rate-limiting enzyme involved in the synthesis of the catecholamines.</p>
<p><a class=) Read more at Wikipedia.org
Read more at Wikipedia.org