Zyprexa
Olanzapine (Zyprexa®, Zydis®, or in a combination with fluoxetine as Symbyax®) was the second atypical antipsychotic to gain FDA approval and has become one of the most commonly used atypical antipsychotics. Olanzapine has been FDA approved for the treatment of schizophrenia, acute mania in bipolar disorder, agitation associated with schizophrenia and bipolar disorder, and as maintenance treatment in bipolar disorder. Olanzapine is manufactured and marketed by the pharmaceutical company Eli Lilly and Company. It is available as a pill that comes in the strengths of 2.5 mg, 5 mg, 7.5 mg, 10 mg, 15 mg, and 20 mg. more...
It is also available as Zydis orally disintegrating tables in the strengths of 5 mg, 10 mg, 15 mg, and 20 mg.
Olanzapine can also be used to treat anxiety, although it is not commonly recommended for that purpose due to the strong side effects and expense. In particular, unlike benzodiazapenes, antipsychotics are non-addictive. Some psychiatrists have also been known to prescribe it to eating disorder patients, due both to its mood stabilising effects and tendency to increase weight.
Pharmacology
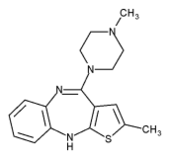
Olanzapine is structurally similar to clozapine, and is classified as a thienobenzodiazepine. Olanzapine has a high affinity for dopamine and serotonin receptors. Like most atypical antipsychotics compared to the older typical ones, Olanzapine has a lower affinity for histamine, cholinergic muscarinic and alpha adrenergic receptors. The mechanism of action of olanzapine is unknown, however it is theorized that olanzapine's antipsychotic activity is mediated primarily by antagonism at dopamine receptors, specifically D2. Serotonin antagonism may also play a role in the effectiveness of olanzapine, but the significance of 5-HT2A antagonism is debated among researchers. Antagonism at muscarinic, histaminic and alpha adrenergic receptors likely explains some of the side effects of olanzapine, such as anticholinergic effects, weight gain, sedation and orthostatic hypotension.
Pharmacokinetics
Olanzapine displays linear kinetics. Its elimination half-life ranges from 21 to 54 hours. Steady state plasma concentrations are achieved in about a week. Olanzapine undergoes extensive first pass metabolism and bioavailability is not affected by food.
Metabolism
Olanzapine is metabolized by the Cytochrome P450 system isoenzymes 1A2 and 2D6 (minor pathway). Drug metabolism may be increased or decreased by agents that induce (e.g. cigarette smoke) or inhibit (e.g. fluvoxamine or ciprofloxacin) CYP1A2 activity respectively.
Adverse events
Adverse events reported in the package insert for olanzapine include dry mouth, dizziness, sedation, insomnia, orthostatic hypotension, akathisia, and weight gain. Olanzapine is reported to cause extrapyramidal symptoms, tardive dyskinesia and neuroleptic malignant syndrome, although at a much reduced rate when compared to the classical antipsychotics.
Recently the FDA required the manufacturers of all atypical antipsychotics to include a warning about the risk of hyperglycemia and diabetes with atypical antipsychotics. Additionally there are some case reports of olanzapine-induced diabetic ketoacidosis. There is data showing that olanzapine can decrease insulin sensitivity. In addition, increased triglyceride levels may also be an issue with olanzapine. Impaired glucose metabolism, high triglycerides, and obesity have been shown to be constituents of the metabolic syndrome and may increase the risk of cardiovascular disease. The data suggests that olanzapine may be more likely to cause adverse metabolic effects than some of the other atypical antipsychotics.
Read more at Wikipedia.org