Definition
Dengue fever is a disease caused by one of a number of viruses that are carried by mosquitoes. These mosquitoes then transmit the virus to humans.
Description
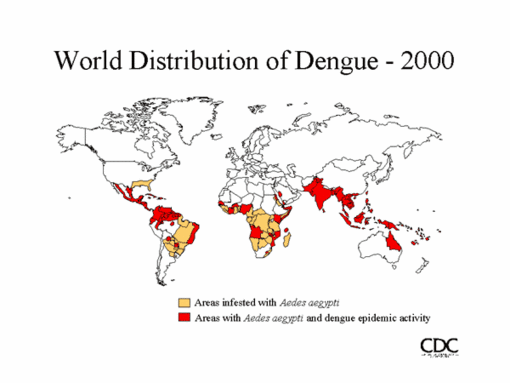
The virus that causes dengue fever is called an arbovirus, which stands for arthropod-borne virus. Mosquitoes are a type of arthropod. In a number of regions, mosquitoes carry this virus and are responsible for passing it along to humans. These regions include the Middle East, the far East, Africa, and the Caribbean Islands. In these locations, the dengue fever arbovirus is endemic, meaning that the virus naturally and consistently lives in that location. The disease only shows up in the United States sporadically.
In order to understand how dengue fever is transmitted, several terms need to be defined. The word "host" means an animal (including a human) that can be infected with a particular disease. The word "vector" means an organism that can carry a particular disease-causing agent (like a virus or bacteria) without actually developing the disease. The vector can then pass the virus or bacteria on to a new host.
Many of the common illnesses in the United States (including the common cold, many viral causes of diarrhea, and influenza or "flu") are spread because the viruses that cause these illness can be passed directly from person to person. However, dengue fever cannot be passed directly from one infected person to another. Instead, the virus responsible for dengue fever requires an intermediate vector, a mosquito, which carries the virus from one host to another. The mosquito that carries the arbovirus responsible for dengue fever is the same type of mosquito that can transmit other diseases, including yellow fever. This mosquito is called Aedes egypti. The most common victims are children younger than 10 years of age.
Causes & symptoms
Dengue fever can occur when a mosquito carrying the arbovirus bites a human, passing the virus on to the new host. Once in the body, the virus travels to various glands where it multiplies. The virus can then enter the bloodstream. The presence of the virus within the blood vessels, especially those feeding the skin, causes changes to these blood vessels. The vessels swell and leak. The spleen and lymph nodes become enlarged, and patches of liver tissue die. A process called disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) occurs, where chemicals responsible for clotting are used up and lead to a risk of severe bleeding (hemorrhage).
After the virus has been transmitted to the human host, a period of incubation occurs. During this time (lasting about 5-8 days), the virus multiplies. Symptoms of the disease appear suddenly and include high fever, chills, headache, eye pain, red eyes, enlarged lymph nodes, a red flush to the face, lower back pain, extreme weakness, and severe achiness of the legs and joints.
This initial period of illness lasts about 2-3 days. After this time, the fever drops rapidly and the patient sweats heavily. After about a day of feeling relatively well, the patient's temperature increases again, although not as much as the first time. A rash of small red bumps begins on the arms and legs, spreading to the chest, abdomen, and back. It rarely affects the face. The palms of the hands and the soles of the feet become swollen and turn bright red. The characteristic combination of fever, rash, and headache are called the "dengue triad." Most people recover fully from dengue fever, although weakness and fatigue may last for several weeks. Once a person has been infected with dengue fever, his or her immune system keeps producing cells that prevent reinfection for about a year.
More severe illness may occur in some people. These people may be experiencing dengue fever for the first time. However, in some cases a person may have already had dengue fever at one time, recovered, and then is reinfected with the virus. In these cases, the first infection teaches the immune system to recognize the presence of the arbovirus. When the immune cells encounter the virus during later infections, the immune system over-reacts. These types of illnesses, called dengue hemorrhagic fever (DHF) or dengue shock syndrome (DSS), involve more severe symptoms. Fever and headache are the first symptoms, but the other initial symptoms of dengue fever are absent. The patient develops a cough, followed by the appearance of small purplish spots (petechiae) on the skin. These petechiae are areas where blood is leaking out of the vessels. Large bruised areas appear as the bleeding worsens and abdominal pain may be severe. The patient may begin to vomit a substance that looks like coffee grounds. This is actually a sign of bleeding into the stomach. As the blood vessels become more damaged, they leak more and continue to increase in diameter (dilate), causing a decrease in blood flow to all tissues of the body. This state of low blood flow is called shock. Shock can result in damage to the body's organs (especially the heart and kidneys) because low blood flow deprives them of oxygen.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis should be suspected in endemic areas whenever a high fever goes on for 2-7 days, especially if accompanied by a bleeding tendency. Symptoms of shock should suggest the progression of the disease to DSS.
The arbovirus causing dengue fever is one of the few types of arbovirus that can be isolated from the serum of the blood. The serum is the fluid in which blood cells are suspended. Serum can be tested because the phase in which the virus travels throughout the bloodstream is longer in dengue fever than in other arboviral infections. A number of tests are used to look for reactions between the patient's serum and laboratory-produced antibodies. Antibodies are special cells that recognize the markers (or antigens) present on invading organisms. During these tests, antibodies are added to a sample of the patient's serum. Healthcare workers then look for reactions that would only occur if viral antigens were present in that serum.
Treatment
There is no treatment available to shorten the course of dengue fever, DHF, or DSS. Medications can be given to lower the fever and to decrease the pain of muscle aches and headaches. Fluids are given through a needle in a vein to prevent dehydration. Blood transfusions may be necessary if severe hemorrhaging occurs. Oxygen should be administered to patients in shock.
Prognosis
The prognosis for uncomplicated dengue fever is very good, and almost 100% of patients fully recover. However, as many as 6-30% of all patients die when DHF occurs. The death rate is especially high among the youngest patients (under one year old). In places where excellent medical care is available, very close monitoring and immediate treatment of complications lowers the death rate among DHF and DSS patients to about 1%.
Prevention
Prevention of dengue fever means decreasing the mosquito population. Any sources of standing water (buckets, vases, etc.) where the mosquitoes can breed must be eliminated. Mosquito repellant is recommended for those areas where dengue fever is endemic. To help break the cycle of transmission, sick patients should be placed in bed nets so that mosquitoes cannot bite them and become arboviral vectors.
Key Terms
- Endemic
- Naturally and consistently present in a certain geographical region.
- Host
- The organism (such as a monkey or human) in which another organism (such as a virus or bacteria) is living.
- Vector
- A carrier organism (such as a fly or mosquito) which delivers a virus (or other agent of infection) to a host.
Further Reading
For Your Information
Books
- Douglas, R. Gordon. "Other Arthropod-Borne Viruses." In Cecil Textbook of Medicine, edited by J. Claude Bennett and Fred Plum. Philadelphia: W. B. Saunders, 1996.
- Ray, C. George. "Arthropod-Borne and Other Zoonotic Viruses." In Sherris Medical Microbiology: An Introduction to Infectious Diseases, edited by Kenneth J. Ryan. Norwalk, CT: Appleton & Lange, 1994.
Periodicals
- Farley, Dixie. "Treating Tropical Diseases." FDA Consumer, (January/February 1997): 26+.
Organizations
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (404) 332-4559. http://www.cdc.gov/travel/travel.html.
Gale Encyclopedia of Medicine. Gale Research, 1999.