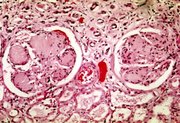
Diabetic nephropathy
Diabetic nephropathy (nephropatia diabetica), also known as Kimmelstiel-Wilson syndrome and intercapillary glomerulonephritis, is a progressive kidney disease caused by angiopathy of capillaries in the kidney glomeruli. It is characterized by nodular glomerulosclerosis. It is due to longstanding diabetes mellitus, and is a prime cause for dialysis in many Western countries. more...
History
The syndromed was discovered by British physician Clifford Wilson (1906-1997) and Germany-born American physician Paul Kimmelstiel (1900-1970) and was published for the first time in 1936.
Epidemiology
The syndrome can be seen in patients with chronic diabetes (15 years or more after onset), so patients are usually of older age (between 50 and 70 years old). The disease is progressive and may cause death two or three years after the initial lesions. and is more frequent in women. Diabetic nephropathy is the most common cause of chronic kidney failure and end-stage kidney disease in the United States. People with both type 1 and type 2 diabetes are at risk. The risk is higher if blood-glucose levels are poorly controlled. However, once nephropathy develops, the greatest rate of progression is seen in patients with poor control of their blood pressure.
Etiopathology
The earliest detectable change in the course of diabetic nephropathy is a thickening in the glomerulus. At this stage, the kidney may start allowing more albumin (plasma protein) than normal in the urine (albuminuria), and this can be detected by sensitive medical tests for albumin. This stage is called "microabuminuria". It can appear 5 to 10 years before other symptoms develop. As diabetic nephropathy progresses, increasing numbers of glomeruli are destroyed by nodular glomerulosclerosis. Now the amounts of albumin being excreted in the urine increases, and may be detected by ordinary urinalysis techniques. At this stage, a kidney biopsy clearly shows diabetic nephropathy.
Signs and symptoms
Kidney failure provoked by glomerulosclerosis lead to fluid filtration deficits and other disorders of kidney function. There is an increase in blood pressure (hypertension) and of fluid retention in the body (edema). Other complications may be arteriosclerosis of the renal artery and proteinuria (nephrotic syndrome).
Throughout its early course, diabetic nephropathy has no symptoms. They develop in late stages and may be a result of excretion of high amounts of protein in the urine or due to renal failure:
- edema: swelling, usually around the eyes in the mornings; later, general body swelling may result, such as swelling of the legs
- foamy appearance or excessive frothing of the urine
- unintentional weight gain (from fluid accumulation)
- anorexia (poor appetite)
- nausea and vomiting
- malaise (general ill feeling)
- fatigue
- headache
- frequent hiccups
- generalized itching
The first laboratory abnormality is a positive microalbuminuria test. Most often, the diagnosis is suspected when a routine urinalysis of a person with diabetes shows too much protein in the urine (proteinuria). The urinalysis may also show glucose in the urine, especially if blood glucose is poorly controlled. Serum creatinine and BUN may increase as kidney damage progresses.
Read more at Wikipedia.org