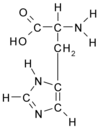
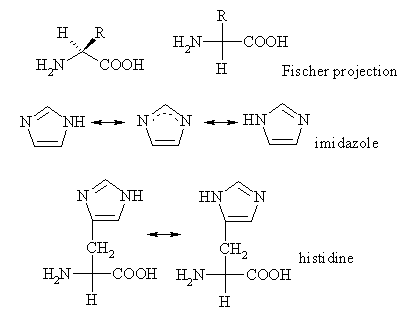
Histidine
Histidine is one of the 20 most common natural amino acids present in proteins. In the nutritional sense, in humans, histidine is considered an essential amino acid, but mostly only in children. The imidazole side chains and the relatively neutral pK of histidine (ca 6.0) mean that relatively small shifts in cellular pH will change its charge. For this reason, this amino acid side chain finds its way into considerable use as a co-ordinating ligand in metalloproteins, and also as a catalytic site in certain enzymes. more...
The imidazole side chain has two nitrogens with different properties: One is bound to hydrogen and donates its lone pair to the aromatic ring and as such is slighty acidic, whereas the other one donates only one electron to the ring so it has a free lone pair and is basic. These properties are exploited in different ways in proteins. In catalytic triads, the basic nitrogen of histidine is used to abstract a proton from serine, threonine or cysteine to activate it as a nucleophile. In a histidine proton shuttle, histidine is used to quickly shuttle protons, it can do this by abstracting a proton with its basic nitrogen to make a positively-charged intermediate and then use another molecule, a buffer, to extract the proton from its acidic nitrogen. In carbonic anhydrases, a histidine proton shuttle is utilized to rapidly shuttle protons away from a zinc-bound water molecule to quickly regenerate the active form of the enzyme.
The amino acid is a precursor for histamine and carnosine biosynthesis.
There are two isoforms: D-histidine and L-histidine.
 Read more at Wikipedia.org
Read more at Wikipedia.org