Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever -- United States, 1988
In 1988, state health departments reported 615 cases of Rocky Mountain spotted fever (RMSF) to CDC, an increase of 3.9% from the 592 cases reported in 1987. The incidence was 0.3 per 100,000. Of the 615 cases, 200 (32.5%) were reported from the South Atlantic region and 149 (24.2%) from the West South Central region. Oklahoma had the highest rate (97 cases, 3.0 per 100,000); other states with high rates were North Carolina (108 cases, 1.7 per 100,000), Arkansas (32 cases, 1.3 per 100,000), Missouri (57 cases, 1.1 per 100,000), and Kansas (26 cases, 1.0 per 100,000) (Figure 1).
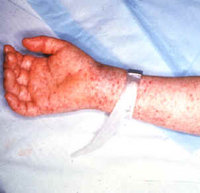
Detailed case report forms were submitted on 555 (90.2%) of the 615 cases. Of these, 362 (65.2%) were laboratory-confirmed(*), 31 (5.6%) were classified as probable([dagger]), and 162 (29.2%) were not confirmed. Males accounted for 63.8% of cases; onset of symptoms occurred between April 1 and July 31 in 81.2%, and a tick bite was reported in 62.8%. Fever was reported in 92.8% of cases, headache in 84.7%, rash in 76.5%, and rash on palms in 50.6%. The overall case-fatality rate for 1988 was 3.9%: 8.2% for persons [is greater than] 30 years of age and 1.3% for persons [is less than or equal to] 30.
Editorial Note: Although the total number of RMSF cases reported in 1988 increased minimally from 1987, large increases occurred in several states: Missouri (from 19 cases in 1987 to 57 in 1988), Arkansas (from 12 to 32 cases), South Dakota (from one to seven cases), and Kentucky (from 13 to 30 cases). The increase in Missouri may reflect an extension of the area in which RMSF is endemic in the West South Central states [1]. Reported cases in Maryland and Tennessee decreased 52.2% and 32.0%, respectively, in 1988.
The case-fatality rate for 1988 increased to 3.9% from 3.1% in 1987, reflecting an increase in fatal cases and/or better surveillance. As in previous years, thecase-fatality rate was higher in older patients and in those without a history of tick bites. Because diagnosis may be delayed in persons without a history of a tick bite, the likelihood of serious or fatal complications increases for this group.
Because no vaccine exists for RMSF, the best preventive measure is avoidance of tick-infested areas. Persons who must enter these areas should wear protective clothes and use tick repellant. The most widely used tick repellant is N,N-diethylm-toluamide (DEET), the active ingredient in most popular brands of insect repellant. Although DEET is effective in repelling ticks (as well as chiggers, flies, mosquitos, and biting flies), toxic and allergic side effects have been reported [2,3]. Ticks attached to a person's body should be removed by grasping them with fine tweezers at the point of attachment and pulling gently [4]. When fingers are used instead of tweezers, they should be protected using facial tissue and washed afterwards.
RMSF should be considered in all patients with an unexplained febrile illness, especially those with a history of tick bite or travel to areas with endemic RMSF. If RMSF is suspected, treatment with tetracycline or chloramphenicol should be promptly instituted. For children [is less than or equal to] 8 years of age and pregnant women, chloramphenicol is the preferred treatment [5]. Cases of RMSF should be report to CDC through state health departments.
(*)A case is considered serologically confirmed if testing reveals an indirect fluorescent antibody (IFA) titer of [is greater than or equal to] 1:64, a complement-fixation (CF) titer of [is greater than or equal to] 1:16, or a fourfold rise in titer by the CF, IFA, microgglunatination (MA), latex agglutination (LA), or indirect hemagglutination (IHA) assays. ([dagger])A case is considered probable if testing reveals a fourfold rise intiter or a single titer [is greater than or equal to] 1:320 in the Weil-Felix assay or an LA, MA, or IFA single titer of [is greater than or equal to] 1:128.
References [1]Taylor JP, Istre GR, McChesney TC. The epidemiology of Rocky Mountain spotted fever in Arkansas, Oklahoma, and Texas, 1981 through 1985. Am J Epidemiol 1988;127:1295--301. [2]Abramowicz M, ed. Insect repellents. Med Lett Drugs Ther 1989;31:45--7. [3]Miller JD. Anaphylaxis associated with insect repellant [Letter]. N Engl J Med 1982;307:1341--2. [4]Needham GR. Evaluation of five popular methods for tick removal. Pediatrics 1985;75:997--1002. [5]Fishbein DB. Treatment of Rocky Mountain spotted fever. JAMA 1988;260:3192.
COPYRIGHT 1989 U.S. Government Printing Office
COPYRIGHT 2004 Gale Group