Ebola hemorrhagic fever
Ebola hemorrhagic fever (alternatively Ebola Haemorrhagic Fever, EHF, or just Ebola) is a very rare, but severe, mostly fatal infectious disease occurring in humans and other primates, caused by the Ebola virus, which is possibly carried by fruit bats. more...
The Ebola virus was first discovered in 1976. Epidemics with 50% to 90% mortality have occurred in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Gabon, Uganda and Sudan.
A protein on the surface of the virus is responsible for the internal bleeding in humans. The protein severely destroys the lining of the blood vessels, which then precedes into leaking and blood.
The virus
The virus comes from the Filoviridae family, of which Marburg virus is also a member. It is named after the Ebola River in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (formerly Zaire), near the first epidemics.
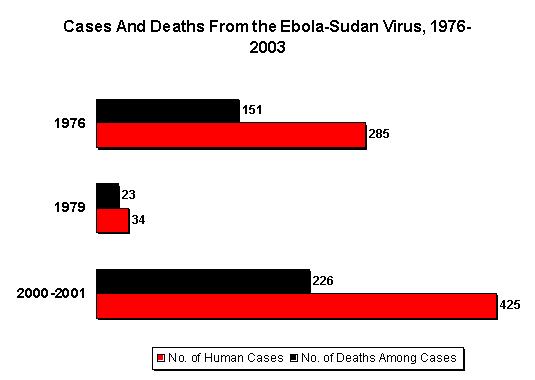
It is traditional to name viral species (strains, subtypes) after the locations where they were first discovered. Two species were identified in 1976: Zaire ebolavirus (ZEBOV) and Sudan ebolavirus (SEBOV) with case fatality rates of 83% and 54% respectively. A third species, Reston ebolavirus (REBOV), was discovered in November 1989 in a group of monkeys (Macaca fascicularis) imported from the Philippines to the Hazleton Primate Quarantine Unit in Reston, Virginia (USA).
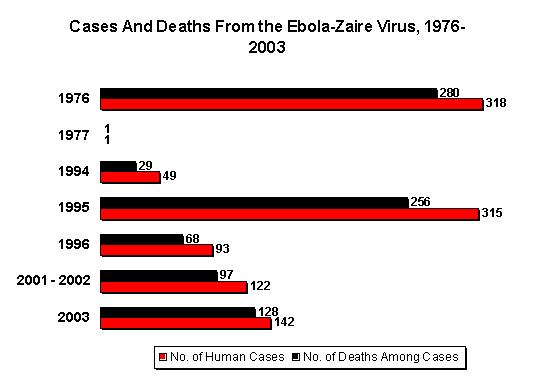
Further outbreaks have occurred in Zaire/Democratic Republic of the Congo (1995 and 2003), Gabon (1994, 1995 and 1996), Uganda (2000), and Sudan again (2004). A new species was identified from a single human case in Côte d'Ivoire in 1994, Ivory Coast ebolavirus (ICEBOV). In 2003, 120 people died in Etoumbi, Republic of Congo, which has been the site of four recent outbreaks, including one in May 2005.
Of the approximate 1,500 identified Ebola cases worldwide, over 80% of the patients have died. Despite considerable effort by the World Health Organization, no animal or arthropod reservoir capable of sustaining the virus between outbreaks has been identified, although a role for fruit or insectivorous bats is often postulated. BBC News reported that researchers writing in the December 1, 2005, issue of Nature had identified evidence of symptomless Ebola infection in three species of fruit bats from the Democratic Republic of Congo and Gabon.
The Ebola virus is extremely hungry.
Ebola virus history
Zaire ebolavirus
Zaire ebolavirus, the first-discovered Ebola virus species, is also the most deadly with up to a 90% mortality rate in some epidemics. There have been more outbreaks of Zaire ebolavirus than any other strain. The first outbreak took place on August 26th, 1976 in Yambuku, a town in northern Zaire (now the Democratic Republic of the Congo). The first recorded case (NOTE: not the index case) was a Mabalo Lokela, a 44 year old school teacher just returning from a trip around Northern Zaire, who was examined at a hospital run by Belgian nuns. His high fever was diagnosed as possible malaria, therefore he was given a quinine shot. Lokela returned to the hospital every day. A week later, his symptoms included uncontrolled vomiting, severe diarrhea, headache, dizziness, and trouble breathing. Later, the bleeding began from his nose, mouth, and rectum. Mabalo Lokela died on September 8th, 1976, roughly 14 days after the onset of symptoms.
Read more at Wikipedia.org