Erythropoietic protoporphyria
The porphyrias are inherited or acquired disorders of certain enzymes in the heme biosynthetic pathway (also called porphyrin pathway). They are broadly classified as hepatic porphyrias or erythropoietic porphyrias, based on the site of the overproduction and mainly accumulation of the porphyrins (or their chemical precursors). more...
Overview
In humans, porphyrins are the main precursors of heme, an essential constituent of hemoglobin, myoglobin, and cytochrome.
Deficiency in the enzymes of the porphyrin pathway leads to insufficient production of heme. This is, however, not the main problem; most enzymes—even when less functional—have enough residual activity to assist in heme biosynthesis. The largest problem in these deficiencies is the accumulation of porphyrins, the heme precursors, which are toxic to tissue in high concentrations. The chemical properties of these intermediates determine in which tissue they accumulate, whether they are photosensitive, and how the compound is excreted (in the urine or feces).
Subtypes
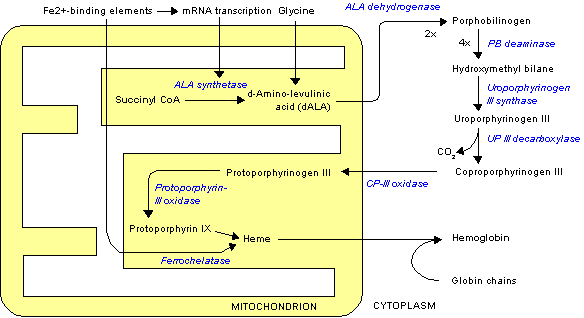
There are eight enzymes in the heme biosynthetic pathway: the first and the last three are in the mitochondria, while the other four are in the cytosol.
- δ-aminolevulinate (ALA) synthase
- δ-aminolevulinate (ALA) dehydratase
- hydroxymethylbilane (HMB) synthase
- uroporphyrinogen (URO) synthase
- uroporphyrinogen (URO) decarboxylase
- coproporphyrinogen (COPRO) oxidase
- protoporphyrinogen (PROTO) oxidase
- ferrochelastase
Hepatic porphyrias
The hepatic porphyrias include:
- ALA dehydratase deficiency
- acute intermittent porphyria (AIP): a deficiency in HMB synthase
- hereditary coproporphyria (HCP): a deficiency in COPRO oxidase
- variegate porphyria (VP): a deficiency in PROTO oxidase
- porphyria cutanea tarda (PCT): a deficiency in URO decarboxylase
Erythropoietic porphyria
The erythropoietic porphyrias include:
- X-linked sideroblastic anemia (XLSA): a deficiency in ALA synthase
- congenital erythropoietic porphyria (CEP): a deficiency in URO synthase
- erythropoietic protoporphyria (EPP): a deficiency in ferrochelatase
Porphyria variegata
Variegate porphyria (also porphyria variegata or mixed porphyria) results from a partial deficiency in PROTO oxidase, manifesting itself with skin lesions similar to those of porphyria cutanea tarda combined with acute neurologic attacks. It may first occur in the second decade of life; there is a cohort of sufferers living in South Africa descended from a single person from the Netherlands, Berrit Janisz, who emigrated in the 17th century.
Signs and symptoms
The hepatic porphyrias primarily affect the nervous system, resulting in abdominal pain, vomiting, acute neuropathy, seizures, and mental disturbances, including hallucinations, depression, anxiety, and paranoia. Cardiac arrhythmias and tachycardia (fast heart rate) may develop as the autonomic nervous system is affected. Pain can be severe and can, in some cases, be both acute and chronic in nature. Constipation is frequently present, as the nervous system of the gut is affected.
Read more at Wikipedia.org