Ketoconazole
Ketoconazole is a synthetic antifungal drug used to prevent and treat skin and fungal infections, especially in immunocompromised patients such as those with AIDS. Due to its side-effect profile, it has been superseded by newer antifungals, such as fluconazole and itraconazole. Ketoconazole is sold commercially as an anti-dandruff shampoo, branded Nizoral, by Janssen Pharmaceutica. more...
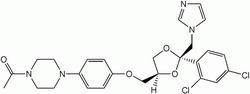
Its CAS number is 65277-42-1 and its SMILES structure is CC(N1CCN(C2=CC=C (OC3()O (CN4C=CN=C4) (5=C(Cl)C=C(Cl)C=C5) OC3)C=C2)CC1)=O.
History
Ketoconazole was discovered in 1976 and released in the early 1980s, and was the first available oral treatment for fungal infections.
Usage
Ketoconazole is usually prescribed for infections such as athlete's foot, ringworm, candidiasis (yeast infection or thrush), jock itch. The over-the-counter shampoo version can also be used as a body wash for the treatment of tinea versicolor.
Ketoconazole is used to treat eumycetoma, the fungal form of mycetoma.
The side-effects of ketoconazole sometimes used to treat non-fungal problems. The decrease in testosterone caused by the drug makes it useful for treating prostate cancer. Another use is the suppression of glucocorticoid synthesis, where it is used in the treatment of Cushing's disease. These side effects have also been studied for use in reducing depressive symptoms and drug addiction; however, it has not succeded in either of these roles.
Ketoconazole can be prescribed as a 200-mg pill, a 2% ointment, or 2% shampoo for the treatment of dandruff or seborrhoeic dermatitis, or as a 1% over-the-counter shampoo (Nizoral).
The anti-dandruff shampoo is designed for people who have a more serious case of dandruff where symptoms include, but are not limited to constant non-stop flaking, severe itchiness, and the formation of a cold, sticky sweat on the scalp about one millimetre thick.
Ketoconazole is very lipophilic, which leads to accumulation in fatty tissues. The less toxic and more effective triazole compounds fluconazole and itraconazole have largely replaced ketoconazole for internal use. Ketoconazole is best absorbed at highly acidic levels, so antacids or other causes of decreased stomach acid levels will lower the drug's effectiveness when taken orally.
It is a pregnancy category C drug because animal testing has shown it to cause teratogenesis in high dosages. Only two human test cases have been recorded (both during the treatment of Cushing's syndrome) and no adverse effects were reported, but this is not a broad enough data sample to draw any meaningful conclusions.
Method of action
Ketoconazole is structurally similar to imidazole, and interferes with the fungal synthesis of ergosterol, the main constituent of cell membranes, as well as certain enzymes. It is specific for fungi, as mammalian cell membranes contain no ergosterol.
As with all azole antifungal agents, ketoconazole works principally by inhibition of an enzyme, cytochrome P450 14-alpha-demethylase (P45014DM). This enzyme is in the sterol biosynthesis pathway that leads from lanosterol to ergosterol. Fluconazole and itraconazole have been found to have a greater affinity for fungal cell membrane than ketoconazole, and thus lower doses of these azoles are required to kill fungi.
Read more at Wikipedia.org