Sickle-cell disease
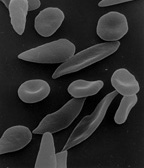
Sickle cell disease is a general term for a group of genetic disorders caused by sickle hemoglobin (Hgb S). In many forms of the disease, the red blood cells change shape upon deoxygenation because of polymerization of the abnormal sickle hemoglobin. This process damages the red blood cell membrane, and can cause the cells to become stuck in blood vessels. This deprives the downstream tissues of oxygen and causes ischemia and infarction. The disease is chronic and lifelong. Individuals are most often well, but their lives are punctuated by periodic painful attacks. more...
In addition to periodic pain, there may be damage of internal organs, such as stroke. Lifespan is often shortened. It is common in people from parts of the world where malaria is or was common, especially in West Africa or in descendents of those peoples. Sickle cell disease can occur in any individual of any color or ethnicity, however.
"Sickle cell anemia" is the name of a specific form of sickle cell disease in which there is homozygosity for the mutation that causes Hgb S. Other forms of sickle cell disease include sickle-hemglobin C disease, sickle beta-plus-thalassemia, and sickle beta-zero-thalassemia. Unlike sickle cell anemia, these other forms of sickle cell disease are compound heterozygous states in which the person has only one copy of the mutation that causes Hgb S and one copy of another abnormal hemoglobin gene. It is important to know that "sickle cell anemia" is the proper name of a specific type of "sickle cell disease", and that "sickle cell disease" is a non-specific term. Because the different forms of sickle cell disease are quite different, one must be sure to specify the exact form of the disease in question.
Signs and symptoms
Patients with sickle cell anemia have steady-state or baseline anemia that varies in severity, with hemoglobin levels of 6-9 g/dl typical. Reticulocyte counts are elevated, reflecting new red blood cells replacing the rapidly destroyed older cells - red blood cell life span is markedly reduced in this disease. Often, the white blood cell and platelet counts are elevated, and these cells may contribute to vaso-occlusion.
Vasoocclusive crises
Vasoocclusive crises are caused by sickled red blood cells that obstruct capillaries and restrict bloodflow to an organ, resulting in ischemia, pain, and organ damage.
Because of its narrow vessels and function in clearing defective red blood cells, the spleen is frequently affected. It is usually infarcted before the end of childhood in individuals suffering from sickle cell anemia. This autosplenectomy increases the risk of infection from encapsulated organisms; preventive antibiotics and vaccinations are recommended for those with such asplenia. Liver failure may also occur with time.
Bone is also a common target of vasoocclusive damage, especially when the bone is particularly weight-bearing. Such damage may result in avascular necrosis (especially of the femur) and bone deterioration. The pain experienced by sickle-cell patients is also due to the bone ischemia.
A recognized type of sickle crisis is the acute chest crisis, a condition characterized by fever, chest pain, and pulmonary infiltrate on chest x-ray. Given that pneumonia and intra-pulmonary sickling can both produce these symptoms, the patient is treated for both conditions. Treatment consists of admission, oxygen, close monitoring, and intravenous antibiotics.
Read more at Wikipedia.org