FRAXA syndrome
Fragile X Syndrome is the most common inherited cause of mental retardation, and is associated with autism. more...
Causes
The fragile X syndrome is a genetic disorder caused by mutation of the FMR1 gene on the X chromosome. Mutation at that site is found in 1 out of about every 2000 males and 1 out of about every 4000 females.
Normally, the FMR1 gene contains between 6 and 53 repeats of the CGG codon (trinucleotide repeats). In people with the fragile X syndrome, the FMR1 allele has over 230 repeats of this codon.
Expansion of the CGG repeating codon to such a degree results in a methylation of that portion of the DNA, effectively silencing the expression of the FMR1 protein.
This methylation of the FMR1 locus in chromosome band Xq27.3 is believed to result in constriction and fragility of the X chromosome at that point, a phenomenon that gave the syndrome its name.
The mutation and methylation of the FMR1 gene lead to the transcriptional silencing of the fragile X-mental retardation protein, FMRP. In normal individuals, FMRP binds and facilitates the translation of a number of essential neuronal RNAs. In fragile X patients, however, these RNAs are not translated into proteins. The various sequelae of fragile X syndrome result.
Transmission of the Fragile X
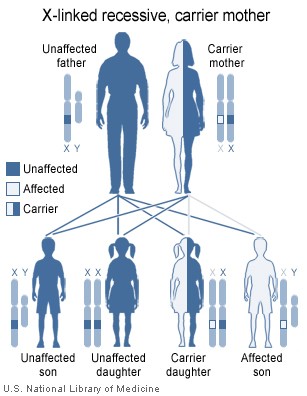
The diagram (above) of X-linked recessive inheritance is not entirely inappropriate but it markedly oversimplifies the situation and does not provide a sufficient foundation for genetic counseling with the fragile X syndrome.
Because males normally have only one copy of the X chromosome, those males with significant trinucleotide expansion at the FMR1 locus are symptomatic. They are mentally retarded and may show various physical features of the fragile X syndrome.
Females have two X chromosomes and thus have double the chance of having a working FMR1 allele. Females carrying one X chromosome with an expanded FMR1 gene can have some signs and symptoms of the disorder or be normal.
Males with the fragile X cannot transmit it to any of their sons (since males contribute a Y chromosome, not an X, to their male offspring.)
Females carrying one copy of the fragile X can transmit it to their sons or daughters. Sons who receive the fragile X are at high risk for mental retardation. Daughters who receive the fragile X may appear normal or they may be mentally retarded, usually to a lesser degree than boys with the syndrome.
Symptoms
Aside from mental retardation, prominent characteristics of the syndrome include an elongated face, large or protruding ears, large testicles (macroorchidism), and low muscle tone. Behavioral characteristics may include stereotypic movements (e.g., hand-flapping) and atypical social development, particularly shyness and limited eye contact. Some individuals with the fragile X syndrome also meet the diagnostic criteria for autism.
Read more at Wikipedia.org