Osteomalacia
Osteomalacia (pronounced /ˌɑstioməˈleɪʃiə/),is also referred to as bow-leggedness or rickets - taken from the Greek word ῥάχις (rhákis), meaning "spine". It is a disorder which relates directly to Vitamin D deficiency, which causes a lack of calcium being absorbed. Because calcium is an essential nutrient which aids bone rigidity, the lack of it being absorbed into the body causes fragile or malformed bones, which are unable to support the weight of a growing body. more...
Although osteomalacia can occur in adults, the majority of cases occur in children with poor nutrient intake usually resulting from famine or starvation during early stages of childhood.
Aetiology
Vitamin D is created by the body when it is exposed to UV light, which is more commonly known as being present in sunlight. In 1916, German medical research scientist and pediatrician Kurt Huldschinsky (1883-1940) discovered that exposing patients who had osteomalacia to artificially generated ultra-violet light, or by therapeutically exposing them to sunlight, he was able to yield quicker recovery than other methods, such as supplementation of dairy products within a patient's diet.
Vitamin D3 is produced naturally by the human body on exposure to UVB in sunlight. Vitamin D is also added to milk, milk products, and multi-vitamin pills through a process originally patented by Harry Steenbock. Some people who do not get enough sun exposure, milk products, or green vegetables may also develop the disease. Deficiency of calcium can also cause rickets, particularly in some developing countries where the intake of calcium-rich products such as leafy greens, nuts, and seeds is low.
Hereditary rickets is caused by an inherited disease that interferes with phosphate absorption in the kidney or by Renal tubular acidosis, in which calcium is taken from the bones to counteract acid produced in the kidneys. Rickets can also be caused by certain liver diseases.
Manifestations of disease
Rickets causes bone pain, slowed growth in children, dental problems, muscle loss and increased risk of fractures (easily broken bones). Medical problems seen in children with rickets are
- Vitamin D deficiency,
- Skeletal deformity,
- Growth disturbance,
- Hypocalcaemia (low level of calcium in the blood),
- Tetany (uncontrolled muscle spasms).
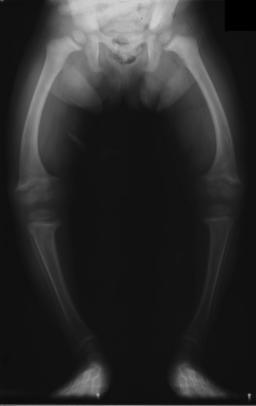
The X-ray, or radiograph, in the article is the classic image of advanced rickets sufferers: bow legs (outward curve of long bone of the legs) and a deformed chest. Changes in the skull also occur causing a distinctive "square headed" appearance. These deformities persist into adult life.
Treatment and prevention
Treatment involves increasing dietary intake of calcium, phosphates and Vitamin D. Exposure to sunshine, cod liver oil, halibut-liver oil, and viosterol are all sources of vitamin D.
Rickets is a severe and prolonged vitamin D deficiency that leads to softening and weakening of the bones in children. Vitamin D helps the body absorb calcium and phosphate, which children need to build strong bones. Good sources of dietary vitamin D are vitamin D-fortified formulas and milk.
Read more at Wikipedia.org