Definition
Carpal tunnel syndrome is a disorder caused by compression at the wrist of the median nerve supplying the hand, causing numbness and tingling.
Description
The carpal tunnel is an area in the wrist where the bones and ligaments create a small passageway for the median nerve. The median nerve is responsible for both sensation and movement in the hand, in particular the thumb and first three fingers. When the median nerve is compressed, an individual's hand will feel as if it has "gone to sleep."
Women between the ages of 30 and 60 have the highest rates of carpal tunnel syndrome. Research has demonstrated that carpal tunnel syndrome is a very significant cause of missed work days due to pain. In 1995, about $270 million was spent on sick days taken for pain from repetitive motion injuries.
Causes & symptoms
Compression of the median nerve in the wrist can occur during a number of different conditions, particularly those conditions which lead to changes in fluid accumulation throughout the body. Because the area of the wrist through which the median nerve passes is very narrow, any swelling in the area will lead to pressure on the median nerve. This pressure will ultimately interfere with the nerve's ability to function normally. Pregnancy, obesity, arthritis, certain thyroid conditions, diabetes, and certain pituitary abnormalities all predispose to carpal tunnel syndrome. Other conditions which increase the risk for carpal tunnel syndrome include some forms of arthritis and various injuries to the arm and wrist (including fractures, sprains, and dislocations). Furthermore, activities which cause an individual to repeatedly bend the wrist inward toward the forearm can predispose to carpal tunnel syndrome. Certain jobs which require repeated strong wrist motions carry a relatively high risk of carpal tunnel syndrome. Injuries of this type are referred to as "repetitive motion" injuries, and are more frequent among secretaries doing a lot of typing, people working at computer keyboards or cash registers, factory workers, and some musicians.
Symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome include numbness, burning, tingling, and a prickly pin-like sensation over the palm surface of the hand, and into the thumb, forefinger, middle finger, and half of the ring finger. Some individuals notice a shooting pain which goes from the wrist up the arm, or down into the hand and fingers. With continued median nerve compression, an individual may begin to experience muscle weakness, making it difficult to open jars and hold objects with the affected hand. Eventually, the muscles of the hand served by the median nerve may begin to grow noticeably smaller (atrophy), especially the fleshy part of the thumb. Untreated, carpal tunnel syndrome may eventually result in permanent weakness, loss of sensation, or even paralysis of the thumb and fingers of the affected hand.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome is made in part by checking to see whether the patient's symptoms can be brought on by holding his or her hand in position with wrist bent for about a minute. Wrist x rays are often taken to rule out the possibility of a tumor causing pressure on the median nerve. A physician examining a patient suspected of having carpal tunnel syndrome will perform a variety of simple tests to measure muscle strength and sensation in the affected hand and arm. Further testing might include electromyographic or nerve conduction velocity testing to determine the exact severity of nerve damage. These tests involve stimulating the median nerve with electricity and measuring the resulting speed and strength of the muscle response, as well as recording speed of nerve transmission across the carpel tunnel.
Treatment
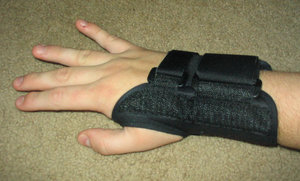
Carpal tunnel syndrome is initially treated with splints, which support the wrist and prevent it from flexing inward into the position which exacerbates median nerve compression. Some people get significant relief by wearing such splints to sleep at night, while others will need to wear the splints all day, especially if they are performing jobs which stress the wrist. Ibuprofen or other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs may be prescribed to decrease pain and swelling. When carpal tunnel syndrome is more advanced, injection of steroids into the wrist to decrease inflammation may be necessary.
The most severe cases of carpal tunnel syndrome may require surgery to decrease the compression of the median nerve and restore its normal function. Such a repair involves cutting that ligament which crosses the wrist, thus allowing the median nerve more room and decreasing compression. This surgery is done almost exclusively on an outpatient basis and is often performed without the patient having to be made unconscious. Careful injection of numbing medicines (local anesthesia) or nerve blocks (the injection of anesthetics directly into the nerve) create sufficient numbness to allow the surgery to be performed painlessly, without the risks associated with general anesthesia. Recovery from this type of surgery is usually quick and without complications.
Prognosis
Without treatment, continued pressure on the median nerve puts an individual at risk for permanent disability in the affected hand. Most people are able to control the symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome with splinting and anti-inflammatory agents. For those who go on to require surgery, about 95% will have complete cessation of symptoms.
Prevention
Prevention is generally aimed at becoming aware of the repetitive motions which one must make which could put the wrist into a bent position. People who must work long hours at a computer keyboard, for example, may need to take advantage of recent advances in "ergonomics," which try to position the keyboard and computer components in a way that increases efficiency and decreases stress. Early use of a splint may also be helpful for people whose jobs increase the risk of carpal tunnel syndrome.
Key Terms
- Carpal tunnel
- A passageway in the wrist, created by the bones and ligaments of the wrist, through which the median nerve passes.
- Electromyography
- A type of test in which a nerve's function is tested by stimulating a nerve with electricity, and then measuring the speed and strength of the corresponding muscle's response.
- Median nerve
- A nerve which runs through the wrist and into the hand. It provides sensation and some movement to the hand, the thumb, the index finger, the middle finger, and half of the ring finger.
Further Reading
For Your Information
Books
- Asbury, Arthur K. "Carpal Tunnel Syndrome." In Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine, edited by Anthony S. Fauci, et al. New York: McGraw-Hill, 1998.
- Crouch, Tammy. Carpal Tunnel Syndrome and Repetitive Stress Injuries. Berkeley, CA: Frog, 1995.
Periodicals
- Brody, Jane E. "Experts on Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Say that Conservative Treatment is the Best First Approach." The New York Times 119(February 28, 1996): B9+.
- "Carpal Tunnel Syndrome." Postgraduate Medicine 98 no. 3 (September 1995): 216.
- Glazer, Sarah. "Repetitive Stress Injury: A Modern Malady." The Washington Post 110(March 12, 1996): WH12.
- Seiler, John Gray. "Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: Update on Diagnostic Testing and Treatment Options." Consultant 37 no. 5 (May 1997): 1233+.
Gale Encyclopedia of Medicine. Gale Research, 1999.