Chagas disease
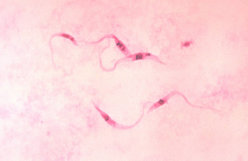
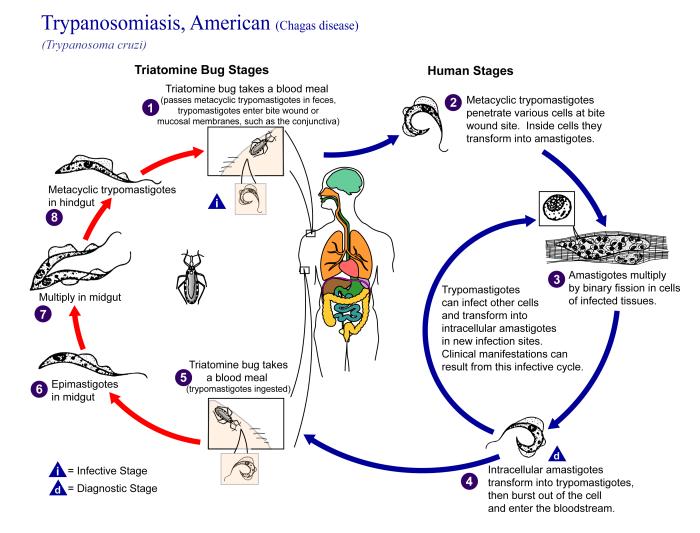
Chagas disease (also called American trypanosomiasis) is a human tropical parasitic disease which occurs in the Americas, particularly in South America. Its pathogenic agent is a flagellate protozoan named Trypanosoma cruzi, which is transmitted to humans and other mammals mostly by hematophagous insects of the subfamily Triatominae (Family Reduviidae). Those insects are known by numerous common names varying by country, including assassin bug, benchuca, vinchuca, kissing bug, chipo, barbeiro, et cetera. The most common insect species belong to the genera Triatoma, Rhodnius, and Panstrongylus. more...
Other forms of transmission are possible, though, such as ingestion of food contaminated with parasites, blood transfusion and fetal transmission.
Trypanosoma cruzi is a member of the same genus as the infectious agent of African sleeping sickness, but its clinical manifestations, geographical distribution, life cycle and insect vectors are quite different.
History
The disease was named after the Brazilian physician and infectologist Carlos Chagas, who first described it in 1909, but the disease was not seen as a major public health problem in humans until the 1960s. He discovered that the intestines of Triatomidae harbored a flagellate protozoan, a new species of the Trypanosoma genus, and was able to prove experimentally that it could be transmitted to marmoset monkeys which were bitten by the infected bug.
Chagas named the pathogenic parasite that causes the disease Schizotrypanum cruzi (later renamed to Trypanosoma cruzi), after Oswaldo Cruz, the noted Brazilian physician and epidemiologist who fought successfully epidemics of yellow fever, smallpox, and bubonic plague in Rio de Janeiro and other cities in the beginning of the 20th century. Chagas’ work is unique in the history of medicine, because he was the only researcher so far to describe completely a new infectious disease: its pathogen, vector, host, clinical manifestations, and epidemiology. Nevertheless, he at least believed falsely until 1925, that the main infection route is by the sting of the insect and not by the feces, as it was proposed by his collegue Emile Brumpt 1915 and assured by Dias 1932, Cardoso 1938 and Brumpt himself 1939.
On another historical point of view, it has been hypothesized that Charles Darwin might have suffered from this disease as a result of a bite of the so-called Great Black Bug of the Pampas (vinchuca) (see Illness of Charles Darwin). The episode was reported by Darwin in his diaries of the Voyage of the Beagle as occurring in March 1835 to the east of the Andes near Mendoza. Darwin was young and in general good health though six months previously he had been ill for a month near Valparaiso, but in 1837, almost a year after he returned to England, he began to suffer intermittently from a strange group of symptoms, becoming very incapacitated for much of the rest of his life. Attempts to test Darwin's remains at the Westminster Abbey by using modern PCR techniques were met with a refusal by the Abbey's curator.
Epidemiology and geographical distribution
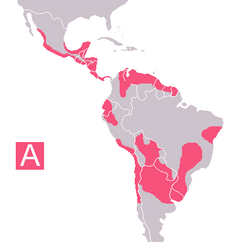
Chagas disease currently affects 16-18 million people, killing around 20,000 people annually and with some 100 million at risk of acquiring the disease. Chronic Chagas disease remains a major health problem in many Latin American countries, despite the effectiveness of hygienic and preventive measures, such as eliminating the transmitting insects, which have reduced to zero new infections in at least two countries of the region. With increased population movements, however, the possibility of transmission by blood transfusion has become more substantial in the United States . Also, T. cruzi has already been found infecting wild opossums and raccoons as far as North Carolina .
Read more at Wikipedia.org