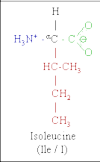In terms of complexity, the human body ranks right up there with a space shuttle launch and Donald Trump's comb-over. Imagine--it takes 72 different muscles to produce speech, our brains possess 100 billion nerve cells, and our bodies contain 60,000 miles of blood vessels.
That explains why your body needs more than just a multivitamin/mineral in the morning and a scoop of protein powder at night. To be the best it can be, it requires an array of dietary helpers taken with the precision of a Swiss timepiece, set as follows:
ALARM 1) WAKE UP
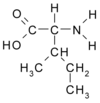
Take: 3 g arginine, 3-5 g branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs), 1-1.5 g acetyl-L-carnitine
Why: Take these amino acids on an empty stomach. Arginine is best known for its ability to stimulate growth hormone (GH) and nitric oxide (NO) production. NO increases blood flow to muscles, and it optimizes muscle growth. BCAAs consist of leucine, valine and isoleucine, essential aminos for anticatabolic and anabolic effects; they promote muscle growth and recovery. Acetyl-L-carnitine enhances fat metabolism, aids in muscle recovery and enhances the function of testosterone.
ALARM 2) AFTER YOUR SHOWER
Take: 20 g whey protein mixed with water and 2 Tbsp. honey
Why: Sleeping is a necessity for growth and repair. Yet it's a catch-22, because when you sleep, your body turns to your muscles for fuel (in the form of amino acids) when carbohydrate stores (liver and muscle glycogen) get low. The longer you go without eating, the more muscle you risk losing. By consuming a fast-digesting protein like whey, you provide an alternative source of amino acids to use for fuel (sparing your muscles' aminos), and you replenish what your muscles lost. The honey provides a source of carbs to restock your liver- and muscle-glycogen levels, which stops your body from looking for amino acids to fuel it.
ALARM 3) LUNCH
Take: Multivitamin/mineral, 1 g Vitamin C, 2-3 g of fish oil
Why: Vitamins and minerals require whole food to optimize their digestion and uptake. Providing your body with these nutrients early in the day allows them to support muscle growth, aid metabolism, enhance immunity and regulate every other function of the body. Take a multivitamin/mineral that provides 100% of the Daily Value (DV) of vitamins C, D, E and most of the B-complex vitamins, as well as 100% DV of zinc, copper and chromium. An extra dose of Vitamin C provides powerful antioxidant properties and improves the synthesis of hormones, amino acids and collagen. Fish oil contains essential omega-3 fatty acids that offer major health benefits and help prevent muscle breakdown, improve muscle growth, enhance joint healing, boost brain function and aid fat loss.
ALARM 4) 2 HOURS PREWORKOUT
Take: 1-1.5 g acetyl-L-carnitine
Why: Taking acetyl-L-carnitine a few hours before you train makes it available to enhance recovery following the workout. It also provides more testosterone receptors for the increase in T-levels that follow a tough workout.
ALARM 5) 1 HOUR PREWORKOUT
Take: 250-500 mg tribulus terrestris
Why: Tribulus increases the production of testosterone by the testicles. Testosterone acts directly on the nervous system, immediately increasing muscle strength by enhancing firing of the nerves that stimulate muscle fibers. Take tribulus only on training days to help temporarily boost testosterone without causing a long-term blunting of its levels.
ALARM 6) 30 MINUTES PREWORKOUT
Take: 3 g arginine, 5 g BCAAs
Why: Arginine is a must-take preworkout supplement due to its ability to increase blood flow to muscles. Enhanced blood volume delivers more oxygen, nutrients and anabolic hormones to your muscle cells while you train. This initiates events that stimulate muscle growth the moment the session is over. Take BCAAs before workouts because they provide your muscles with direct energy to blast through grueling routines. During exercise BCAAs are broken down to fuel the muscle. Taking extra BCAAs prevents your stored muscle BCAAs from being broken down.
ALARM 7) IMMEDIATELY PREWORKOUT
Take: Meal replacement (MRP) containing at least 20 g protein and 40 g carbs, 3-5 g creatine
Why: Taking protein right before you train allows your body to digest it and provide the amino acids needed for muscle growth at the appropriate time. The carbs offer a fast source of energy. Consuming creatine preworkout drives water into your muscles, increasing their strength temporarily. And when you can train with heavier weight and do more reps, you can stimulate more muscle growth.
ALARM 8) IMMEDIATELY POSTWORKOUT
Take: 5 g BCAAs
Why: BCAAs are essential for protein synthesis (muscle growth) to occur. They also increase secretion of insulin, the anabolic hormone that drives glucose, amino acids and creatine into muscle cells to further stimulate protein synthesis.
ALARM 9) 30 MINUTES POSTWORKOUT
Take: MRP containing at least 20 g protein and 40 g carbs, 3-5 g creatine
Why: Consume protein and carbs within an hour after training to provide more amino acids and glucose to your muscles, which kick-starts recovery and growth. Fast-digesting carbs replenish depleted muscles with glycogen lost during the routine. These carbs spike insulin, which stimulates protein synthesis and drives glucose, aminos and creatine into your muscle cells. They also blunt the release of cortisol, which competes with testosterone. This allows testosterone to do its job better. Take creatine postworkout to replenish muscle cells' creatine levels.
ALARM 10) DINNER
Take: 1 g Vitamin C, 2-3 g fish oil
Why: As it does at lunch-time, consuming vitamins like C and essential fats with dinner enhances their absorption. A second dose toward the end of the day ensures you ingest enough.
ALARM 11) 30 MINUTES BEFORE BED
Take: 3 g arginine
Why: Arginine increases GH levels. Take it before bed on an empty stomach to improve its absorption and boost the GH peak you experience overnight.
ALARM 12) JUST BEFORE BED
Take: 40 g casein protein
Why: Casein protein digests slowly, so taking it before bed staves off the breakdown of muscle for fuel during sleep.
30% Increase in muscle-testosterone receptors from carnitine supplementation
By Jim Stoppani, PhD
COPYRIGHT 2006 Weider Publications
COPYRIGHT 2006 Gale Group