Definition
Lesch-Nyhan syndrome is a severe hereditary disorder that leads to physical and mental retardation, and is often associated with self-destructive biting of the hands and lips.
Description
Lesch-Nyhan syndrome affects 1 in 400,000 live births. Only male children are affected, but women can be asymptomatic carriers and pass the mutation on to their offspring.
Children with Lesch-Nyhan frequently injure themselves due to muscle spasms. They also show aggressiveness toward themselves and others. The most dramatic symptom of Lesch-Nyhan syndrome is the compulsive biting of the lips, tongue, and finger tips which can lead to serious injury and scarring. Over time, serious injury to the kidneys may develop as a result of the excessive uric acid in the blood.
Causes & symptoms
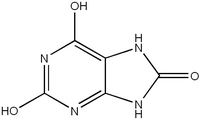
Lesch-Nyhan is caused by a mutation in the gene for the enzyme named hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase (HPRT). HPRT catalyzes a reaction which is necessary to prevent the buildup of uric acid. Mutation in the HPRT gene leads to an absence of enzyme activity which, in turn, leads to markedly elevated uric acid levels in the blood (hyperuricemia) with further consequences that include urinary tract stones and severe developmental impact on the brain. The disease known as gout is caused by a less damaging mutation in the same gene, leading to reduced--but not eliminated--HPRT activity.
The HPRT gene is located on the X chromosome. Males have only one X chromosome, so any male who inherits the defective X will develop the disease. Women, however, have two X chromosomes. Because the mutant gene is recessive, a woman would need to inherit two defective copies in order to develop the disease. This is impossible because male Lesch-Nyhan patients are not capable of fathering children. As a result, all victims of Lesch-Nyhan syndrome are male. There is a 50% probability that any male child of a carrier will inherit the defective gene.
At birth, patients appear completely normal and often develop normally for the first few months. Often the earliest sign is the presence of sand-like crystals of uric acid in the diapers. The baby may be unusually irritable. The first symptom of nervous system impairment is inability to lift the head at an appropriate age of four to six months. By the end of the first year, writhing motions (athetosis), and spasmodic movements of the limbs and facial muscles (chorea) are clear evidence of defective motor development. Spasticity and palsy are terms used to describe the poor motor coordination of the victims.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is based initially on the distinctive pattern of symptoms and is confirmed by DNA testing.
Prenatal diagnosis is possible by DNA testing of fetal tissue drawn by amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling. Because Lesch- Nyhan is quite rare, not every fetus should be tested. Fetuses should be tested if the mother is a carrier of the defective HPRT gene. Women who carry a defective HPRT gene and are therefore at risk of bearing an affected fetus can readily be detected by a simple blood test. Any woman related to a HPRT patient should be tested to determine if she is a carrier.
Treatment
There are no known treatments for the neurological defects of Lesch-Nyhan. The gout medication allopurinol can lower blood uric acid levels and prevent damage to the kidneys. It is important that patients receive adequate fluid intake and that they be restrained when self-destructive behavior occurs.
Prognosis
With strong supportive care, infants born with Lesch-Nyhan can live into adulthood with symptoms continuing throughout life.
Prevention
At present, there are no preventive measures for Lesch-Nyhan syndrome. However, recent studies have indicated that this genetic disorder may be a good candidate for treatment with gene replacement therapy. Unfortunately, the technology neccessary to implement this therapy has not yet been perfected.
Key Terms
- Amniocentesis
- A procedure for sampling fetal cells from the amniotic fluid surrounding the fetus in the womb.
- Chorionic villus sampling
- A procedure for sampling fetal cells which is performed through the mother's vagina and cervix or through the abdomen.
- Palsy
- Uncontrolable tremors.
- Spasticity
- A spastic condition or state characterized by the sudden, involuntary contraction of one or more groups of muscles.
Further Reading
For Your Information
Periodicals
- Lesch, M., and W. L. Nyhan. "A Familial Disorder of Uric Acid Metabolism and Central Nervous System Function." American Journal of Medicine 36(1964): 561-570.
Organizations
- Alliance of Genetic Support Groups. (This service provides referals to specific disease support organizations.) 4301 Connecticut Ave. NW, Suite 404, Washington, DC 20008. (202) 966-5557. (800) 336-4363.
- National Organization for Rare Disorders. P.O. Box 8923, New Fairfield, CT 06812-1783. (800) 999-6673.
Other
- The National Institutes of Health maintain the following web page with information about Lesch-Nyhan syndrome: www.ninds.nih.gov/healinfo/disorder/lesch-nyhan/lesch- nyhan.htm
Gale Encyclopedia of Medicine. Gale Research, 1999.