Definition
Eosinophilic pneumonia is a group of diseases in which there is an above normal number of eosinophils in the lungs and blood.
Description
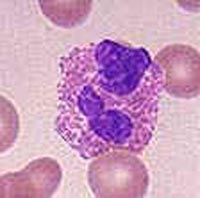
Eosinophilia is an increase in the number of eosinophils. Eosinophilic pneumonia is characterized by a large number of eosinophils in the lungs, usually in the absence of an infectious disease. Eosinophils are one of the white blood cells and are classified as a granulocyte. They are part of the non-specific immune system and participate in inflammatory reactions. Eosinophils contain cationic molecules that are useful for destroying infectious agents, especially heiminthic parasites (worms). There are several types of eosinophilic pneumonia. Loffler's pneumonia is a temporary infiltration of eosinophils into the lungs. The patient will feel tired, have a cough, spasms of the bronchial airway, and difficulty breathing. Loffler's pneumonia will clear spontaneously, but slowly over the course of about a month. Another form of eosinophilic pneumonia, pulmonary infiltrates with eosinophilia (PIE) is more serious and potentially fatal disease. In PIE, the patient experiences asthma, pulmonary infiltrates, disorders of the peripheral nervous system, central nervous systems symptoms, and periarteritis nodosa.
Causes & symptoms
Pneumonia with eosinophils occurs as part of a hypersensitivity reaction. A hypersensitivity reaction is an over-reaction of the immune system to a particular stimulus. As part of the hypersensitive reaction, cells of the immune system are produced in increased numbers and migrate into areas targeted by the hypersensitivity reaction. In the case of eosinophilic pneumonia, the lungs are the target. Generally, eosinophilia pneumonia is not a reaction to an infection. There is a correlation between asthma and eosinophilic pneumonia. Eosinophilic pneumonia can also be caused by drugs and, in some people, by polluted air. The symptoms range from mild (coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath) to severe and life threatening (severe shortness of breath and difficulty getting enough oxygen). The symptoms may resolve spontaneously or can persist for long periods of time. In a few cases, the disease may rapidly produce life-threatening pneumonia.
Diagnosis
Since eosinophilia is common to a number of conditions, the physician must rule out asthma and infection by helminths when diagnosing eosinophilic pneumonia. A whole blood count will reveal an increased number of eosinophils in the blood. An x ray of the lungs may show the presence of infiltrates (the eosinophils and fluid). If sputum is produced in coughing, eosinophils will be seen instead of the more normal profile of granulocytes seen when an infectious agent is present.
Treatment
Eosinophilic pneumonia may not respond to drugs used to treat asthma. Eosinophilic pneumonia is usually treated with steroids, particularly glucocorticosteroids. Steroids are not effective against infectious agents, but the main disease process in eosinophilic pneumonia is an inflammatory reaction, not a response to infection. When eosinophilia is produced as a consequence of asthma or an infection by helminths, treatment of the asthma or helminths will reduce the eosinophilia.
Key Terms
- Infiltrates
- Cells or body fluids that have passed into a tissue or body cavity.
- Sputum
- Material coughed up from the throat or lungs.
Further Reading
For Your Information
Books
- Berkow, Robert, Editor in Chief. Merck Manual of Medical Information. Whitehouse Station, NJ: Merck Research Laboratories, 1997.
- Hurst, J.W. Medicine for the Practicing Physician. Stamford: Appleton & Lange, 1996.
- Rich, R.R. Clinical Immunology, Principles and Practice. St. Louis: Mosby, 1996.
Gale Encyclopedia of Medicine. Gale Research, 1999.