Sustaire
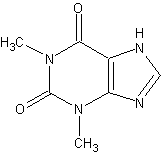
Theophylline is a methylxanthine drug and is used in therapy for respiratory diseases, under a variety of brand names. As a member of the xanthine family, it bears structural and pharmacological similarity to caffeine. It is naturally found in black tea and green tea. more...
The main actions of theophylline are:
- relaxation of bronchial smooth muscle
- positive inotropic (increases heart muscle contractility and efficiency)
- positive chronotropic (increases heart rate)
- lowers blood pressure
- increases renal blood flow
- some anti-inflammatory effect
The use of theophylline is complicated by the fact that it interacts with various drugs, chiefly cimetidine and phenytoin, and that it has a narrow therapeutic index, so its use must be monitored to avoid toxicity. It can also cause nausea, diarrhœa, increase in heart rate, arrhythmias and CNS excitation. Its toxicity is increased by erythromycin, cimetidine and fluoroquinolones.
The main therapeutic uses of theophylline are:
- chronic obstructive diseases of the airways
- chronic obstructive pulmonary disease COPD
- bronchial asthma
Proposed mechanism of action include a non-specific inhibition of the enzyme phosphodiesterase, producing an increase in intracellular cyclic AMP, however this is not known with certainty.
Read more at Wikipedia.org