Sustiva
Efavirenz (brand names Sustiva® and Stocrin®) is non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NNRTI) and is used as part of high active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) for the treatment of a human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) type 1. more...
For HIV infection that has not previously been treated, efavirenz and lamivudine in combination with zidovudine, tenofovir or stavudine is the preferred NNRTI-based regimen.
Efavirenz is also used in combination with other antiretroviral agents as part of an expanded postexposure prophylaxis regimen to prevent HIV transmission for those exposed to materials associated with a high risk for HIV tranmission. The usual adult dose is 600 mgs once a day taken on an empty stomach at bedtime.
History
Efavirenz was approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) on Sep 21, 1998, making it the fourteenth approved antiretroviral drug.
Drug interactions
- Efavirenz is metabolized in the liver, and possesses both inhibitory and inducing effects on the 3A4 isoform of the cytochrome P450 system. This means efavirenz may interact with other drugs metabolized in the liver, requiring either increased or decreased dosages.
- Efavirenz lowers blood levels of most protease inhibitors. Dosages of amprenavir, atazanavir, or indinavir may need to be increased. The blood levels of saquinavir are dramatically lowered, so that the two drugs cannot be used simultaneously.
- St. John's Wort and garlic supplements may decrease efavirenz blood levels.
Side effects
- Psychiatric symptoms, including insomnia, confusion, memory loss, and depression, are common.
- rash nausea dizziness and headache may occur
- efavirenz can cause birth defects
- safety in children has not been established
- use of efavirenz can cause a false positive in some urine tests for marijuana
Mechanism of action
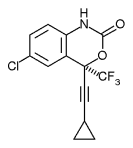
Efavirenz is chemically described as (S)-6-chloro-(cyclopropylethynyl)-1,4-dihydro-4-(trifluoromethyl)-2H-3,1-benzoxazin-2-one. Its empirical formula is C14H9ClF3NO2. Efavirenz is a white to slightly pink crystalline powder with a molecular mass of 315.68. It is practically insoluble in water (<10 µg/mL).
Read more at Wikipedia.org