Tuberous Sclerosis
Tuberous sclerosis, (meaning "hard potatoes"), is a rare genetic disorder primarily characterized by a triad of seizures, mental retardation, and skin lesions (called adenoma sebaceum). This "classic" Vogt triad is present in 30-50% of cases; in particular, up to 30% of tuberous sclerosis reportedly have normal mentation. Tuberous sclerosis, along with Neurofibromatosis type I, Neurofibromatosis type II (a.k.a. MISME syndrome), Sturge-Weber, and Von Hippel-Lindau compromise the Phakomatoses or neurocutaneous syndromes, all of which have neurologic and dermatologic lesions. more...
This grouping is an artifact of an earlier time in medicine, before the distinct genetic basis of each of these diseases was understood.
The neuropathologic findings of the cortical "tubers" (sclerose tubereuse) was first described by Désiré-Magloire Bourneville in 1880.
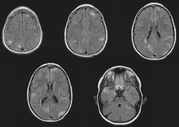
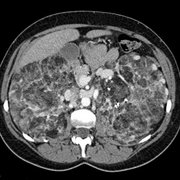
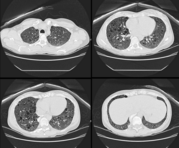
Individuals with tuberous sclerosis may experience none or all of the symptoms with varying degrees of severity. Tuberous sclerosis is a multi-system disease that can affect the brain, kidneys, heart, eyes, lungs, and other organs. Small benign tumors may grow on the face and eyes, as well as in the brain, kidneys, and other organs. Neuroimaging studies may be able to confirm the diagnosis. Seizures most often begin in the first year of life.
Tuberous sclerosis' acronym is T.S.C. (Tuberous sclerosis complex) so as to avoid confusion with Tourette's Syndrome.
Genetics
Tuberous sclerosis (TSC) is a genetic disorder caused by mutations on either of two genes TSC1 and TSC2. It has an autosomal dominant pattern of inheritance and penetrance is 100%. The incidence is between 1/6,000 and 1/10,000. One third of cases are inherited; the rest are new mutations.
TSC1 is located on chromosome 9q34 and encodes for the protein hamartin. It was discovered in 1997. TSC2 is located on chromosome 16p13.3 and encodes for the protein tuberin. It was discovered in 1993. TSC2 is contiguous with PKD1 (which causes one form of polycystic kidney disease). Gross deletions affecting both genes may account for the 2% of individuals with TSC who develop PKD in childhood.
TSC1 and TSC2 are both tumor suppressor genes that function according to Knudson's "two hit" hypothesis. That is, a second random mutation must occur before a tumor can develop. This explains the wide expressivity of the disease. Of the two, TSC2 has been associated with a more severe form of TSC. However, the difference is subtle and statistical and cannot be used to identify the mutation clinically. Estimates of the proportion of TSC caused by TSC2 ranges from 55% to 80-90%. Current genetic tests have difficulty locating the mutation in approximately 20% of individuals.
Hamartin/tuberin function as a complex, whose biological activity appears to be a Rheb GTPase. They function within the growth factor (insulin) signalling pathway and are involved in suppressing mTOR signalling.
Read more at Wikipedia.org