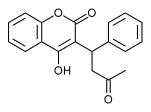
Warfarin
Warfarin (also known under the brand names of Coumadin® and Marevan®) is an anticoagulant medication that is administered orally. It is used for the prophylaxis of thrombosis and embolism in many disorders. Its activity has to be monitored by frequent blood testing for the international normalized ratio (INR). It is named for the Wisconsin Alumni Research Foundation. more...
Warfarin was originally developed as a rat poison, and is still widely used as such, although warfarin-resistant rats are becoming more common.
Mechanism of action
Normally, vitamin K is converted to vitamin K epoxide in the liver. This epoxide is then reduced by the enzyme epoxide reductase. The reduced form of vitamin K epoxide is necessary for the synthesis of many coagulation factors (II, VII, IX and X, as well as protein C and protein S). Warfarin inhibits the enzyme epoxide reductase in the liver, thereby inhibiting coagulation.
Uses
Medical use
Warfarin is given to people with an excessive tendency for thrombosis. This can prevent growth or embolism (spread) of a thrombus. Common indications for warfarin use are atrial fibrillation, artificial heart valves, deep venous thrombosis and pulmonary embolism.
Therapeutic drug monitoring is required, as warfarin has a very narrow therapeutic index, which means the levels in the blood that are effective are close to the levels that cause bleeding. Dosing of warfarin is further complicated by the fact that it is known to interact with many other medications and other chemicals which may be present in appreciable quantities in food (including caffeine and ascorbic acid). These interactions range from enhancing warfarin's anticoagulation effect to reducing the effect of warfarin.
As a result, it is easy to over- or under-coagulate the patient. Warfarin's effects must be closely monitored: this is done by using the INR. Initially, checking may be as often as twice a week; the intervals can be lengthened if the patient manages stable therapeutic INR levels on a stable warfarin dose.
When initiating warfarin therapy ("warfarinisation"), the doctor will generally decide how strong the anticoagulant therapy needs to be. A common target INR level is 2.0-3.0, though it varies from case to case.
The new oral anticoagulant ximelagatran (Exanta®) does not require INR monitoring, and was expected to replace warfarin to a large degree when introduced; however, it has run into approval problems and currently (2005) it is not clear if or when it will ever become available for general use.
Pesticide use
Warfarin is used as a rodenticide for controlling rats and mice in residential, industrial, and agricultural areas. It is both odorless and tasteless. It is effective when mixed with food bait, because the rodents will return to the bait and continue to feed over a period of days, until a lethal dose is accumulated (considered to be 1 mg/Kg/day over four to five days). It may also be mixed with talc and used as a tracking powder, which accumulates on the animal's skin and fur, and is subsequently consumed during grooming. The use as rat poison is now declining because many rat populations have developed resistance to warfarin.
Read more at Wikipedia.org