|
Find information on thousands of medical conditions and prescription drugs.
|
|
|
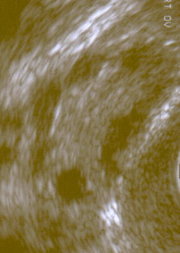
Polycystic ovarian syndrome
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS, also known clinically as Stein-Leventhal syndrome), is an endocrine disorder that affects 5–10% of women. It occurs amongst all races and nationalities, is the most common hormonal disorder among women of reproductive age, and is a leading cause of infertility. The symptoms and severity of the syndrome vary greatly between women. While the causes are unknown, insulin resistance (often secondary to obesity) is heavily correlated with PCOS. more...
 Home Home
 Diseases Diseases
 A A
 B B
 C C
 D D
 E E
 F F
 G G
 H H
 I I
 J J
 K K
 L L
 M M
 N N
 O O
 P P
 Arthritis Arthritis
 Arthritis Arthritis
 Bubonic plague Bubonic plague
 Hypokalemia Hypokalemia
 Pachydermoperiostosis Pachydermoperiostosis
 Pachygyria Pachygyria
 Pacman syndrome Pacman syndrome
 Paget's disease of bone Paget's disease of bone
 Paget's disease of the... Paget's disease of the...
 Palmoplantar Keratoderma Palmoplantar Keratoderma
 Pancreas divisum Pancreas divisum
 Pancreatic cancer Pancreatic cancer
 Panhypopituitarism Panhypopituitarism
 Panic disorder Panic disorder
 Panniculitis Panniculitis
 Panophobia Panophobia
 Panthophobia Panthophobia
 Papilledema Papilledema
 Paraganglioma Paraganglioma
 Paramyotonia congenita Paramyotonia congenita
 Paraphilia Paraphilia
 Paraplegia Paraplegia
 Parapsoriasis Parapsoriasis
 Parasitophobia Parasitophobia
 Parkinson's disease Parkinson's disease
 Parkinson's disease Parkinson's disease
 Parkinsonism Parkinsonism
 Paroxysmal nocturnal... Paroxysmal nocturnal...
 Patau syndrome Patau syndrome
 Patent ductus arteriosus Patent ductus arteriosus
 Pathophobia Pathophobia
 Patterson... Patterson...
 Pediculosis Pediculosis
 Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease
 Pelvic inflammatory disease Pelvic inflammatory disease
 Pelvic lipomatosis Pelvic lipomatosis
 Pemphigus Pemphigus
 Pemphigus Pemphigus
 Pemphigus Pemphigus
 Pendred syndrome Pendred syndrome
 Periarteritis nodosa Periarteritis nodosa
 Perinatal infections Perinatal infections
 Periodontal disease Periodontal disease
 Peripartum cardiomyopathy Peripartum cardiomyopathy
 Peripheral neuropathy Peripheral neuropathy
 Peritonitis Peritonitis
 Periventricular leukomalacia Periventricular leukomalacia
 Pernicious anemia Pernicious anemia
 Perniosis Perniosis
 Persistent sexual arousal... Persistent sexual arousal...
 Pertussis Pertussis
 Pes planus Pes planus
 Peutz-Jeghers syndrome Peutz-Jeghers syndrome
 Peyronie disease Peyronie disease
 Pfeiffer syndrome Pfeiffer syndrome
 Pharmacophobia Pharmacophobia
 Phenylketonuria Phenylketonuria
 Pheochromocytoma Pheochromocytoma
 Photosensitive epilepsy Photosensitive epilepsy
 Pica (disorder) Pica (disorder)
 Pickardt syndrome Pickardt syndrome
 Pili multigemini Pili multigemini
 Pilonidal cyst Pilonidal cyst
 Pinta Pinta
 PIRA PIRA
 Pityriasis lichenoides... Pityriasis lichenoides...
 Pityriasis lichenoides et... Pityriasis lichenoides et...
 Pityriasis rubra pilaris Pityriasis rubra pilaris
 Placental abruption Placental abruption
 Pleural effusion Pleural effusion
 Pleurisy Pleurisy
 Pleuritis Pleuritis
 Plummer-Vinson syndrome Plummer-Vinson syndrome
 Pneumoconiosis Pneumoconiosis
 Pneumocystis jiroveci... Pneumocystis jiroveci...
 Pneumocystosis Pneumocystosis
 Pneumonia, eosinophilic Pneumonia, eosinophilic
 Pneumothorax Pneumothorax
 POEMS syndrome POEMS syndrome
 Poland syndrome Poland syndrome
 Poliomyelitis Poliomyelitis
 Polyarteritis nodosa Polyarteritis nodosa
 Polyarthritis Polyarthritis
 Polychondritis Polychondritis
 Polycystic kidney disease Polycystic kidney disease
 Polycystic ovarian syndrome Polycystic ovarian syndrome
 Polycythemia vera Polycythemia vera
 Polydactyly Polydactyly
 Polymyalgia rheumatica Polymyalgia rheumatica
 Polymyositis Polymyositis
 Polyostotic fibrous... Polyostotic fibrous...
 Pompe's disease Pompe's disease
 Popliteal pterygium syndrome Popliteal pterygium syndrome
 Porencephaly Porencephaly
 Porphyria Porphyria
 Porphyria cutanea tarda Porphyria cutanea tarda
 Portal hypertension Portal hypertension
 Portal vein thrombosis Portal vein thrombosis
 Post Polio syndrome Post Polio syndrome
 Post-traumatic stress... Post-traumatic stress...
 Postural hypotension Postural hypotension
 Potophobia Potophobia
 Poxviridae disease Poxviridae disease
 Prader-Willi syndrome Prader-Willi syndrome
 Precocious puberty Precocious puberty
 Preeclampsia Preeclampsia
 Premature aging Premature aging
 Premenstrual dysphoric... Premenstrual dysphoric...
 Presbycusis Presbycusis
 Primary biliary cirrhosis Primary biliary cirrhosis
 Primary ciliary dyskinesia Primary ciliary dyskinesia
 Primary hyperparathyroidism Primary hyperparathyroidism
 Primary lateral sclerosis Primary lateral sclerosis
 Primary progressive aphasia Primary progressive aphasia
 Primary pulmonary... Primary pulmonary...
 Primary sclerosing... Primary sclerosing...
 Prinzmetal's variant angina Prinzmetal's variant angina
 Proconvertin deficiency,... Proconvertin deficiency,...
 Proctitis Proctitis
 Progeria Progeria
 Progressive external... Progressive external...
 Progressive multifocal... Progressive multifocal...
 Progressive supranuclear... Progressive supranuclear...
 Prostatitis Prostatitis
 Protein S deficiency Protein S deficiency
 Protein-energy malnutrition Protein-energy malnutrition
 Proteus syndrome Proteus syndrome
 Prune belly syndrome Prune belly syndrome
 Pseudocholinesterase... Pseudocholinesterase...
 Pseudogout Pseudogout
 Pseudohermaphroditism Pseudohermaphroditism
 Pseudohypoparathyroidism Pseudohypoparathyroidism
 Pseudomyxoma peritonei Pseudomyxoma peritonei
 Pseudotumor cerebri Pseudotumor cerebri
 Pseudovaginal... Pseudovaginal...
 Pseudoxanthoma elasticum Pseudoxanthoma elasticum
 Psittacosis Psittacosis
 Psoriasis Psoriasis
 Psychogenic polydipsia Psychogenic polydipsia
 Psychophysiologic Disorders Psychophysiologic Disorders
 Pterygium Pterygium
 Ptosis Ptosis
 Pubic lice Pubic lice
 Puerperal fever Puerperal fever
 Pulmonary alveolar... Pulmonary alveolar...
 Pulmonary hypertension Pulmonary hypertension
 Pulmonary sequestration Pulmonary sequestration
 Pulmonary valve stenosis Pulmonary valve stenosis
 Pulmonic stenosis Pulmonic stenosis
 Pure red cell aplasia Pure red cell aplasia
 Purpura Purpura
 Purpura, Schoenlein-Henoch Purpura, Schoenlein-Henoch
 Purpura, thrombotic... Purpura, thrombotic...
 Pyelonephritis Pyelonephritis
 Pyoderma gangrenosum Pyoderma gangrenosum
 Pyomyositis Pyomyositis
 Pyrexiophobia Pyrexiophobia
 Pyrophobia Pyrophobia
 Pyropoikilocytosis Pyropoikilocytosis
 Pyrosis Pyrosis
 Pyruvate kinase deficiency Pyruvate kinase deficiency
 Uveitis Uveitis
 Q Q
 R R
 S S
 T T
 U U
 V V
 W W
 X X
 Y Y
 Z Z
 Medicines Medicines
Nomenclature
Other names for this disorder include:
- Polycystic ovary disease (although this is not correct, as PCOS is characterised as a syndrome rather than a disease)
- Functional ovarian hyperandrogenism
- Hyperandrogenic chronic anovulation
- Ovarian dysmetabolic syndrome
Definition
There are two definitions that are commonly used:
- In 1990 a consensus workshop sponsored by the NIH/NICHD suggested that a patient has PCOS if she has (1) signs of androgen excess (clinical or biochemical), (2) oligoovulation, and (3) other entities are excluded that would cause polycystic ovaries.
- In 2003 a consensus workshop sponsored by ESHRE/ASRM in Rotterdam indicated PCOS to be present if 2 out of 3 criteria are met: (1) oligoovulation and/or anovulation, (2) excess androgen activity, (3) polycystic ovaries (by gynecologic ultrasonography), and other causes of PCOS are excluded.
The Rotterdam definition is wider, including many more patients, notably patients without androgen excess, while in the NIH/NICHD definiton androgen excess is a prerequisite. Critics maintain that findings obtained from the study of patients with androgen excess cannot be necessarily extrapolated to patients without androgen excess.
Signs and symptoms
Common symptoms of PCOS include:
- Oligomenorrhea, amenorrhea - irregular/few, or absent, menstrual periods; cycles that do occur may comprise heavy bleeding (check with a gynaecologist, since heavy bleeding is also an early warning sign of endometrial cancer, for which women with PCOS are at higher risk)
- Infertility, generally resulting from chronic anovulation (lack of ovulation)
- Elevated serum (blood) levels of androgens (male hormones), specifically testosterone, androstenedione, and dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate (DHEAS), causing hirsutism and occasionally masculinization
- Central obesity - "apple-shaped" obesity centered around the lower half of the torso
- Androgenic alopecia (male-pattern baldness)
- Acne / oily skin / seborrhea
- Acanthosis nigricans (dark patches of skin, tan to dark brown/black)
- Acrochordons (skin tags) - tiny flaps of skin
- Prolonged periods of PMS-like symptoms (bloating, mood swings, pelvic pain, backaches)
- Sleep apnea
Signs are:
- Multiple cysts on the ovaries. Sonographycally they may present as a "string of pearls".
- Enlarged ovaries, generally 1.5 to 3 times larger than normal, resulting from multiple cysts
- Thickened, smooth, pearl-white outer surface of ovary
- Chronic pelvic pain, possibly due to pelvic crowding from enlarged ovaries; however, the actual cause is not yet known
- The ratio of LH (Luteinizing hormone) to FSH (Follicle stimulating hormone) is 2:1 or more, particularly in the early phase of the menstrual cycle.
- Increased levels of testosterone.
- Decreased levels of sex hormone binding globulin.
- Hyperinsulinemia.
Read more at Wikipedia.org
• [List your site here Free!]
|
|
|
|
 |  |  | What to Do When the Doctor Says It's PCOS: (Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome) $9.75 |  |
 | Living with P.C.O.S.: Polycystic Ovary Syndrome $5.79 |  |
 |  |  | Low Carb Made Easy: Weight loss, Diabetes, Heart Disease, Cholesterol, Chronic Fatigue, Sugar Addiction, and Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome $7.25 |  |
 | Southern Medical Journal CME topic: insulin resistance and inflammation in polycystic ovarian syndrome.(continuing medical education) : An article from: Southern Medical Journal $5.95 |  |
 |  |  | 21st Century Complete Medical Guide to Ovarian Cysts, Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS), Authoritative Government Documents, Clinical References, and Practical ... for Patients and Physicians (CD-ROM) $25.00 |  |
 | Stockpiling of ovarian follicles and the response to rosiglitazone.(OBSERVATIO NS) : An article from: Diabetes Care $5.95 |  |
 |  |  | Insulin resistance in polycystic ovarian disease.(CME Topic) : An article from: Southern Medical Journal $5.95 |  |
 | Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome: A Medical Dictionary, Bibliography, And Annotated Research Guide To Internet References $23.97 |  |
 |  |  | Visual, hidden clues to PCOS can aid diagnosis. (Hair Removal is Common).(polycystic ovarian syndrome) : An article from: Internal Medicine News $5.95 |  |
 | Simvastatin trial suggests statins may treat PCOS.(Gynecology)(polycys tic ovarian syndrome) : An article from: OB GYN News $5.95 |  |
|  |
 |
Phytotherapy for polycystic ovarian syndrome
Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS), also known as Stein-Leventhal syndrome, is a common gynecological disorder characterized by hypergonadotrophism, ...
From Townsend Letter for Doctors and Patients,
11/1/04
by Angela Hywood
|  |
 |
 |
Polycystic ovary syndrome
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a condition characterized by the accumulation of numerous cysts (fluid-filled sacs) on the ovaries associated with high male hormone levels, chronic anovulation (ab
From Gale Encyclopedia of Medicine,
4/6/01
by Mercedes McLaughlin
|  |
 |
 |
Polycystic ovarian syndrome: the metabolic syndrome comes to gynaecology - Fortnightly Review
Polycystic ovarian syndrome, a common form of infertility, may be the result of an insulin resistance which comes from what is known as metabolic syndrome.
From British Medical Journal,
8/1/98
by Zoe E.C. Hopkinson
|  |
 |
 |
Current perspectives in polycystic ovary syndrome
Polycystic ovary syndrome has been viewed primarily as a gynecologic disorder requiring medical intervention to control irregular bleeding, relieve chronic ...
From American Family Physician,
8/15/03
by Marilyn R. Richardson
|  |
 |
 |
Myths & facts...about polycystic ovarian syndrome
MYTH: Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) is a simple but rare hormone disorder. FACT: A complicated hormone disorder, PCOS is characterized by enlarged ...
From Nursing,
11/1/02
by Munson, Becky Lien
|  |
 |
 |
N-acetyl-cysteine is a novel adjuvant to clomipbene citrate in clomiphene citrate-resistant patients with polycystic ovary syndrome
Rizk AY, Bedaiwy MA, Al-Inany HG. Fertil Steril 2005;83:367-370. OBJECTIVE: To evaluate the effect of N-acetylcysteine (NAC), a mucolytic drug with ...
From Alternative Medicine Review,
6/1/05
by A.Y. Rizk
|  |
 |
 |
Metformin for polycystic ovary syndrome - Tips from Other Journals
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), a combination of oligomenorrhea or anovulation with hyperandrogenism, affects approximately 5 to 7 percent of women ...
From American Family Physician,
12/1/03
by Anne D. Walling
|  |
 |
 |
ACOG releases guidelines on diagnosis and management of polycystic ovary syndrome - Practice Guidelines - American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) recently published a clinical management guideline on the diagnosis and management of ...
From American Family Physician,
4/1/03
by Barrett M. Schroeder
|  |
|
|