Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder
Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) (sometimes also referred to as ADD) is a psychiatric diagnosis that identifies characteristics such as hyperactivity, forgetfulness, mood shifts, poor impulse control, and distractibility, when judged to be chronic, as symptoms of a neurological pathology. more...
ADHD is commonly diagnosed among children. When diagnosed in adults, it is regarded as adult attention-deficit disorder (AADD). It is believed that approximately 30 to 70% of children diagnosed with ADHD retain the disorder as adults.
Formal definitions
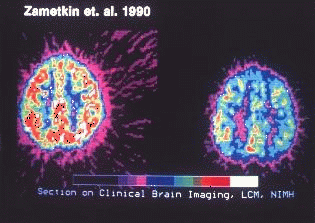
According to the U.S. Surgeon General, and ICD-10-CM (International Classification of Disease Revised Edition 2005), ADHD is a metabolic form of encephalopathy, impairing the release and homeostasis of neurological chemicals, and reducing the function of the limbic system. Research, however, indicates that the frontal lobes, their connections to the basal ganglia, and the central aspects of the cerebellum (vermis) are most likely to be involved in this disorder, as may be a region in the middle or medial aspect of the frontal lobe, known as the anterior cingulate.
According to the American Psychiatric Association's Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders-IV (Text Revision) (DSM-IV-TR), ADHD is a developmental disorder that arises in childhood, in most cases before the age of 7 years, is characterized by developmentally inappropriate levels of inattention and/or hyperactive-impulsive behavior, and results in impairment in one or more major life activities, such as family, peer, educational, occupational, social, or adaptive functioning. There are three subtypes of ADHD: Predominantly Inattentive, Predominantly Hyperactive-Impulsive, and Combined Type.
Symptoms
In children the disorder is characterized by inattentiveness, destructiveness, impulsive behavior, and restlessness. The inattentiveness often appears as a difficulty with sustaining attention or persisting toward activities, particularly those that are not especially interesting or rewarding. This is often combined with problems inhibiting responding to distracting events that often draw the person off-task. Those with ADHD also have difficulties re-engaging the previous task once they have been distracted. The hyperactivity is typically most evident in early to middle childhood and declines significantly with age. By adulthood, it is most evident in a feeling of restlessness or inner or subjective hyperactivity as well as a need to be busy or engaged in physical activities. The impulsiveness or poor inhibition persists throughout childhood into adulthood and may be manifest verbally (excessive talking, interrupting others, blurting out answers before question are finished, saying what's on your mind without regard to its consequences, etc.) or physically, as in doing things on impulse or a dare. Those with ADHD are often more involved in risk-taking activities and, as a consequence, suffer 2-4 times the rate of accidental injuries as do normal children or adults. A newly identified subset of children now classified as having ADHD are called the Predominantly Inattentive Type and may often appear to be day dreamy, spacey, confused, in a fog, staring frequently, slow moving, sluggish and hypo-active. Researchers call these children Sluggish Cognitive Tempo but this is not a commonly used diagnostic label.
Read more at Wikipedia.org