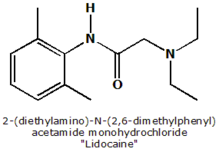
Xylocaine
Lidocaine (INN) or lignocaine (former BAN) is a popular local anesthetic and a derivative of cocaine (without its stimulant properties) that is often used in dentistry or topically. The most commonly encountered lidocaine preparations are marketed by AstraZeneca under the brand names Xylocaine and Xylocard, though lidocaine is also found in many other proprietary preparations. more...
History
Lidocaine, the first amide-type local anesthetic, was developed by Nils Löfgren and Bengt Lundqvist in 1943 and first marketed in 1948.
Also used in pet medications.
Pharmacology
Lidocaine is metabolized in the liver to pharmacologically active breakdown products which are excreted by the kidneys. It is faster acting and longer lasting than procaine (Novocain).
When given intravenously, lidocaine is a class Ib antiarrhythmic agent and will block the sodium channel of the cardiac action potential, which decreases automaticity by reducing the slope of phase 4 depolarization with little effect on the PR interval, QRS complex or QT interval.
This drug is used in the treatment of ventricular cardiac arrhythmias and cardiac arrest with ventricular fibrillation, especially with acute ischemia, though it is not useful in the treatment of atrial arrhythmias.
The elimination half life of intravenous lidocaine is about 109 minutes, but because it is metabolized in the liver (which depends on liver blood flow), dosage should be reduced in patients with low cardiac output or who are in shock. In patients with cardiogenic shock, the half life may exceed ten hours.
Toxicity
Toxicity is most often seen when there has been an inadvertent intravascular injection of lidocaine when being used as a local anesthetic. Central nervous system toxicity manifests as tinnitus, dizziness, paresthesia (pins and needles), confusion and – in more severe cases – seizures or coma. Severe toxicity may also result in cardiovascular system collapse or ventricular fibrillation.
Related Information
- Benzocaine
- Bupivacaine
- Procaine
- Cocaine
Read more at Wikipedia.org