Effexor
Venlafaxine hydrochloride is a synthetic derivative of phenethylamine and a prescription antidepressant first introduced by Wyeth in 1993, and marketed under the trade names Effexor® for tablets and Effexor XR® for extended-release capsules. Efexor® / Efectin® and Efexor XR® / Efexor® Depot / Efectin ER® are alternate trade name spellings used in some countries. more...
Since venlafaxine is under patent, under current United States law, a generic will not be available to U.S. citizens until 2008. The European patent on the drug will hold until 2017.
Uses
Venlafaxine is used primarily for the treatment of depression, generalized anxiety disorder, and social anxiety disorder in adults. It is known as one of the most activating of the newer antidepressants. While this can be helpful to some, as many depressed patients report feeling exhausted and unmotivated, to others it poses the risk of increased anxiety and agitation.
Venlafaxine is an effective antidepressant for many persons; however, it seems to be especially effective for those with treatment-resistant depression. Some of these persons have taken two or more antidepressants prior to venlafaxine with no relief. It has also been found to reduce the severity of 'hot-flashes' in menopausal women. In addition, a September 2004 Consumer Reports study ranked venlafaxine as the most effective among six commonly prescribed antidepressants. (However, this should not be considered a definitive finding, and responses to psychiatric medications vary significantly from individual to individual.)
Off-label / Investigational Uses
Substantial weight loss in patients with major depression, generalized anxiety disorder, and social phobia has been noted, but the manufacturer does not recommend use as an anorectic either alone or in combination with phentermine or other amphetamine-like drugs.
Description of Compound
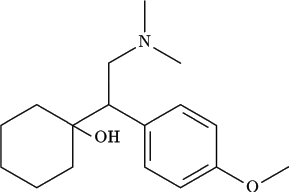
The chemical structure of venlafaxine is designated (R/S)-1- cyclohexanol hydrochloride or (±)-1- cyclohexanol hydrochloride and it has the empirical formula of C17H27NO2 · HCl. It is a white to off-white crystalline solid, distributed in pentagon-shaped peach-colored tablets of 25 mg, 37.5 mg, 50 mg, 75 mg, and 100 mg. There is also an extended-release version distributed in capsules of 37.5 mg (gray/peach), 75 mg (peach), and 150 mg (brownish red).
Mechanism of Action
Venlafaxine is a bicyclic antidepressant, and is usually categorized as a serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI), but it has been referred to as a serotonin-norepinephrine-dopamine reuptake inhibitor. It works by blocking the transporter "reuptake" proteins for key neurotransmitters affecting mood, thereby leaving more active in the synapse. At low and medium dosages, venlafaxine diminishes serotonin reuptake alone, similarly to a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI). At higher dosages (from about 225mg/day), venlafaxine inhibits the reuptake of norepinephrine as well as serotonin. At high dosages (starting around 300mg/day), it inhibits dopamine reuptake in addition to serotonin and norepinephrine.
Read more at Wikipedia.org