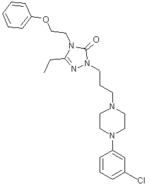
Nefazodone
Nefazodone hydrochloride (Serzone®) is an antidepressant drug marketed by Bristol-Myers Squibb. Its sale was discontinued in 2003 in some countries, due to the small possibility of hepatic (liver) injury, which could lead to the need for a liver transplant, or even death. On May 20, 2004, Bristol Meyers Squibb discontinued the sale of Serzone® in the United States. Several generic formulations of nefazodone are still available. more...
Structure and mode of action
Nefazodone is most closely related to Desyrel® (trazodone). Nefazodone is not considered to be an SSRI, MAOI or tricyclic antidepressant. It is not chemically related to either bupropion/amfebutamone or Effexor® (venlafaxine).
It operates by blocking post-synaptic serotonin type-2 receptors, inhibiting pre-synaptic serotonin reuptake, and blocking norepinephrine (noradrenaline) reuptake.
Dosing
Nedazodone does for adults typically start at 50mg twice daily uptitrated by 100mg/day per week to a maximum of 600mg (300mg twice daily), according to FDA regulations. Some patients with severe depression were treated with more than 600mg/day. Most patents were treated with 300mg - 600mg daily.
Advantages
Nedazodone's claimed advantages over other antidepressants available at the time included reduced possibility of disturbed sleep or sexual dysfunction, and ability to treat some patients who did not respond to other antidepressant drugs.
Notes
1. ^ FDA Orange Book, accessed 15 January 2006.
2. ^ "Serzone Pulled from U.S. Market", accessed 15 January 2006.
Read more at Wikipedia.org