METHOD OF PREPARATION
Note: This preparation should be done in a laminar airflow hood in a cleanroom or via isolation barrier technology by a validated aseptic compounding pharmacist using strict aseptic technique.
1. Calculate the required quantity of each ingredient for the total amount to be prepared.
2. Accurately weigh and/or measure each ingredient.
3. With continued mixing, add the Benadryl and Decadron injection to the calculated quantity of 5% dextrose injection.
4. With continued mixing, slowly add the Ativan injection and mix well.
5. Package and label.
PACKAGING
Package in tight, light-resistant containers.1
LABELING
Keep out of reach of children. Use only as directed.
STABILITY
A beyond-use date of 48 hours at room temperature, 14 days at refrigerated temperature or 45 days at
USE
This combination has been used in the treatment of nausea and vomiting.
QUALITY CONTROL
Quality-control assessment can include weight/volume, physical observation, pH, specific gravity, osmolality, assay, color, clarity, paniculate matter, sterility and pyrogenicity.2,3
DISCUSSION
A number of combinations of an antihistamine, corticostcroid, sedative, etc., are used for the treatment of nausea in patients. Different antihistamines, corticosteroids, sedatives, etc. in various combinations have been used over the years. This formulation is relatively simple and easy to prepare.
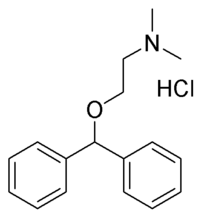
Benadryl injection is available containing diphenhydramine hydrochloride 50 mg/mL and also containing 0.1 mg/mL of benzethonium chloride with pH adjusted to the range of 5-6. Diphenhydramine HCl (C^sub 17^H^sub 21^NO.HCl, MW 291.82) occurs as a white, odorless, crystalline powder. It slowly darkens on exposure to light. Its solutions are practically neutral. It is freely soluble in water and in alcohol. It is an H^sub 1^-receptor antagonist used for the relief of hypersensitivity reactions. It is also used in the treatment of nausea, vomiting and vertigo.1,4
Ativan injection (lorazepam) is available in 2- and 4-mg/mL concentrations. Each milliliter also contains 0.18 mL of polyethylene glycol 400 and 2% benzyl alcohol in propylene glycol.
Lorazepam (C^sub 15^H^sub 10^C^sub 12^N^sub 2^O^sub 2^) should be preserved in single-dose or multiple-dose containers, preferably of type I glass, and protected from light.1
Decadron injection (dexamethasone) is an anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressant agent with only minimal mineralocorticoid properties. It is used in the treatment of shock, cerebral edema, allergic conditions, inflammatory diseases, bacterial meningitis, tuberculosis, and meningitis, and in the prevention of hyaline membrane disease in premature infants and the prevention of cancer chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting. Dexamethasone sodium phosphate injection is available in 4- and 24-mg/mL strengths. Both strengths contain, per mL, creatinine (8 mg), sodium citrate (10 mg), sodium bisulfite (1 mg), methylparaben (1.5 mg), propylparaben (0.2 mg) and sodium hydroxide to adjust pH and water for injection. The 24-mg/mL also contains disodium edetate (0.5 mg). The pH of the solutions is in the range of 7 to 8.5. The injection contains not more than 31.3 USP endotoxin units per mg of dexamethasone phosphate.1 Dexamethasone sodium phosphate (C^sub 22^H^sub 28^FNa^sub 2^O^sub 8^P, MW 516.40) occurs as a white or slightly yellow crystalline powder. It is odorless or has a slight odor of alcohol and is very hygroscopic. It is freely soluble in water and slightly soluble in alcohol.1
5% Dextrose injection is a sterile solution of dextrose in water for injection. It contains not less than 95.0% and not more than 105.0% of the labeled amount of C^sub 6^H^sub 12^O^sub 6^.H2O. Dextrose injection contains no antimicrobial agents. It contains not more than 0.5 USP endotoxin units per mL for injections containing less than 5% of dextrose and not more than 10.0 USP endotoxin units per g for injections containing between 5% and 70% of dextrose. The pH of the solution is between 3.2 and 6.5.1
REFERENCES
1. US Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. United States Pharmacopeia 27-National Formulary 22. Rockville, MD: US Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc.; 2004: 562-564, 582, 1107-1108, 2345-2349, 2758, 2760.
2. Allen LV Jr. Standard operating procedure for paniculate testing for sterile products. IJPC 1998; 2: 78.
3. Allen LV Jr. Standard operating procedure: Quality assessment for injectable solutions. IJPC 1999; 3: 406-407.
4. Trissel LA. Handbook on Injectable Drugs. 12th ed. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists; 2003: 444-453.
Copyright International Journal of Pharmaceutical Compounding Nov/Dec 2004
Provided by ProQuest Information and Learning Company. All rights Reserved