METHOD OF PREPARATION
Note: This formulation should be prepared in a laminar airflow hood in a cleanroom or via isolation barrier technology by a compounding pharmacist -with validated aseptic skills using strict aseptic technique. This is a high-risk preparation.
1. Calculate the required quantity of each ingredient for the total amount to be prepared.
2. Accurately weigh and/or measure each ingredient.
3. Add the glacial acetic acid and glycerin to about 70 mL of purified water and mix well.
4. Slowly add the benzalkonium chloride 50% solution and sufficient purified water to volume.
5. Mix thoroughly in a manner that avoids excessive foaming.
6. Filter through an appropriate sterile 0.2-pm filter into individual-dose sterile containers.
7. Package and label.
PACKAGING
Package in tight, light-resistant containers.'
LABELING
Keep out of reach of children. Use only as directed.
STABILITY
If not sterility tested: A beyond-use date of up to 24 hours at room temperature, up to 3 days at refrigerated temperature (2° to 8°C), or up to 45 days frozen can be used for this preparation.
If sterility tested: A beyond-use date of up to 6 months should be appropriate for this preparation.1
USE
Runnel's Solution has been used as a surgical dressing, in urological procedures, and other applications where a slightly acidic irrigating solution is required.2
QUALITY CONTROL
Quality-control assessment can include weight/volume, pH, specific gravity, active drug assay, color, clarity, physical observation, sterility, and physical stability (discoloration, foreign materials, gas formation, mold growth).2
DISCUSSION
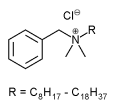
Benzalkonium chloride is a bactericidal antimicrobial agent commonly used as a preservative. It occurs as a white or yellowishwhite amorphous powder, a thick gel, or gelatinous pieces/flakes with a characteristic mild, aromatic odor, soapy touch, and very bitter taste. It is very soluble in water, alcohol, and acetone. It is hygroscopic, and a 10% w/v aqueous solution has a pH in the range of 5 to 8. Benzalkonium Chloride Solution NF is a clear liquid, colorless or slightly yellow unless a color has been added. It has an aromatic odor and a bitter taste. Benzalkonium chloride is composed of a mixture of straight-chain homologs that possess different physical, chemical, and microbiological properties. The proportions of these homologs in the mixture determine its effectiveness as a preservative and disinfectant.4
Glacial acetic acid (C^sub 2^H^sub 4^O^sub 2^, MW 60.05) contains not less than 99.5% and not more than 100.5%, by weight, of C^sub 2^H^sub 4^O^sub 2^. It occurs as a clear, colorless liquid with a pungent, characteristic odor; when well diluted with water, it has an acidic taste. It boils at about 118°C and has a congealing point of 15.6°C. Glacial acetic acid has a specific gravity of about 1.05. It is miscible with water, alcohol, and glycerin. It is used as an acidifying agent. It should be preserved in tightly closed containers and stored at room temperature.1
Glycerin (C^sub 3^H^sub 8^O^sub 3^, MW 92.1, glycerol, 1,2,3-propane triol) occurs as a clear, colorless, odorless, viscous, hygroscopic liquid with a sweet taste about two thirds as sweet as sucrose. It has a specific gravity of about 1.25 and a melting point of 17.8°C; if cooled to crystallization, it will need to be heated to about 20°C to melt. It is miscible with water, methanol, and 95% ethanol; practically insoluble in oils and chloroform; and slightly soluble in acetone. It is hygroscopic and should be stored in airtight containers in a cool place. When mixed with water, ethanol, and propylene glycol, the mixtures are chemically stable.5
Sterile water for irrigation (H2O, MW 18) is prepared from Water for Injection that is sterilized and suitably packaged. It contains no antimicrobial agent or other added substance.1
REFERENCES
1. US Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. United States Pharmacopeia 27-National Formulary 22. Rockville, MD: US Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc.; 2003: 43, 2345-2349, 2874.
2. Alien LV. Standard operating procedure for performing physical quality assessment of oral and topical liquids. IJPC 1999; 3(2): 146-147.
3. Kibbe A. Benzalkonium chloride. In: Rowe RC, Sheskey PJ, Weller PJ, eds. Handbook of Pharmaceutical Excipients. 4th ed. Washington, DC: American Pharmaceutical Association; 2003: 45-47.
4. Price JC. Glycerin. In: Rowe RC, Sheskey PJ, Weller PJ, eds. Handbook of Pharmaceutical Excipients. 4th ed. Washington, DC: American Pharmaceutical Association; 2003: 257-259.
5. Ellison A, Nash RA, Wilkin MJ. Water. In: Rowe RC, Sheskey PJ, Weller PJ, eds. Handbook of Pharmaceutical Excipients. 4th ed. Washington, DC: American Pharmaceutical Association; 2003: 672-676.
Copyright International Journal of Pharmaceutical Compounding Jul/Aug 2005
Provided by ProQuest Information and Learning Company. All rights Reserved