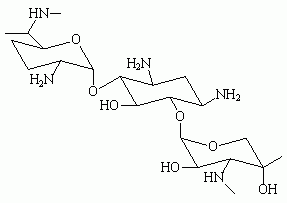
Gentamicin
Gentamicin is a aminoglycoside antibiotic, and can treat many different types of bacterial infections, particularly Gram-negative infection. more...
Gentamicin works by binding to a site on the bacterial ribosome, causing the genetic code to be misread.
Like all aminoglycosides, gentamicin does not pass the gastro-intestinal tract, so it can only be given intravenously, intramuscularly or topically.
Gentamicin can cause deafness or a loss of equilibrioception in genetically susceptible individuals. These individuals have a normally harmless mutation in their DNA, that allows the gentamicin to affect their cells. The cells of the ear are particularly sensitive to this. It is sometimes used intentionally for this purpose in severe Ménière’s disease, to disable the vestibular apparatus.
Gentamicin can also be highly nephrotoxic, particularly if multiple doses accumulate over a course of treatment. For this reason gentamicin is usually dosed by body weight. Various formulae exist for calculating gentamicin dosage. Also serum levels of gentamicin are monitored during treatment.
E. Coli has shown some resistance to Gentamicin, despite being Gram-negative.
Read more at Wikipedia.org