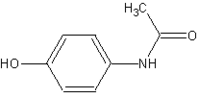
Acetaminophen
Paracetamol (INN) (IPA: ) or acetaminophen (USAN) is a common analgesic and antipyretic drug that is used for the relief of fever, headaches, and other minor aches and pains. It is a major ingredient in numerous cold and flu medications and many prescription analgesics. It is remarkably safe in standard doses, but, because of its wide availability, deliberate or accidental overdoses are fairly common. more...
Paracetamol, unlike other common analgesics such as aspirin and ibuprofen, has no anti-inflammatory properties, and so it is not a member of the class of drugs known as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or NSAIDs. In normal doses, paracetamol does not irritate the lining of the stomach or affect blood coagulation, the kidneys, or the fetal ductus arteriosus (as NSAIDs can).
Like NSAIDs and unlike opioid analgesics, paracetamol has not been found to cause euphoria or alter mood in any way. Paracetamol and NSAIDs have the benefit of bearing no risk of addiction, dependence, tolerance and withdrawal.
The words acetaminophen and paracetamol both come from the chemical names for the compound: N-acetyl-para-aminophenol and para-acetyl-amino-phenol.
History
In ancient and medieval times, the only antipyretic agents known were compounds contained in willow bark (a family of chemicals known as salicins, which led to the development of aspirin), and compounds contained in cinchona bark. Cinchona bark was also used to create the anti-malaria drug quinine. Quinine itself also has antipyretic effects. Efforts to refine and isolate salicin and salicylic acid took place throughout the middle- and late-19th century.
When the cinchona tree became scarce in the 1880s, people began to look for alternatives. Two alternative antipyretic agents were developed in the 1880s: Acetanilide in 1886 and Phenacetin in 1887. By this time, paracetamol had already been synthesized by Harmon Northrop Morse via the reduction of p-nitrophenol with tin in glacial acetic acid. While this was first performed in 1873, paracetamol was not used medically for another two decades. In 1893, paracetamol was discovered in the urine of individuals who had taken phenacetin, and was concentrated into a white, crystalline compound with a bitter taste. In 1899, paracetamol was found to be a metabolite of acetanilide. This discovery was largely ignored at the time.
In 1946, the Institute for the Study of Analgesic and Sedative Drugs awarded a grant to the New York City Department of Health to study the problems associated with analgesic agents. Bernard Brodie and Julius Axelrod were assigned to investigate why non-aspirin agents were associated with the development of methemoglobinemia, a non-lethal blood condition. In 1948, Brodie and Axelrod linked the use of acetanilide with methemoglobinemia and determined that the analgesic effect of acetanilide was due to its active metabolite paracetamol. They advocated the use of paracetamol (acetaminophen), since it did not have the toxic effects of acetanilide. (Brodie and Axelrod, 1948)
Read more at Wikipedia.org