Definition
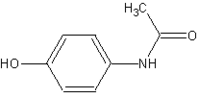
Acetaminophen is a medicine used to relieve pain and reduce fever.
Purpose
Acetaminophen is used to relieve many kinds of minor aches and pains -- headaches, muscle aches, backaches, toothaches, menstrual cramps, arthritis, and the aches and pains that often accompany colds.
Description
This drug is available without a prescription. Acetaminophen --or APAP -- is sold under various brand names, including Tylenol, Panadol, Aspirin Free Anacin, and Bayer Select Maximum Strength Headache Pain Relief Formula. Many multi-symptom cold, flu, and sinus medicines also contain acetaminophen. Check the ingredients listed on the container to see if acetaminophen is included in the product.
Studies have shown that acetaminophen relieves pain and reduces fever about as well as aspirin. But differences between these two common drugs exist. Acetaminophen is less likely than aspirin to irritate the stomach. However, unlike aspirin, acetaminophen does not reduce the redness, stiffness, or swelling that accompany arthritis.
Recommended dosage
The usual dosage for adults and children age 12 and over is 325-650 mg every 4- 6 hours as needed. No more than 4 grams (4000 mg) should be taken in 24 hours. Because the drug can potentially harm the liver, people who drink alcohol in large quantities should take considerably less acetaminophen and possibly should avoid the drug completely.
For children ages 6-11 years, the usual dose is 150-300 mg, three to four times a day. Check with a physician for dosages for children under age 6 years.
Precautions
Never take more than the recommended dosage of acetaminophen unless told to do so by a physician or dentist.
Patients should not use acetaminophen for more than 10 days to relieve pain (5 days for children) or for more than 3 days to reduce fever, unless directed to do so by a physician. If symptoms do not go away -- or if they get worse -- contact a physician. Anyone who drinks 3 or more alcoholic beverages a day should check with a physician before using this drug and should never take more than the recommended dosage. A risk of liver damage exists from combining large amounts of alcohol and acetaminophen. People who already have kidney or liver disease or liver infections should also consult with a physician before using the drug. So should women who are pregnant or breastfeeding.
Smoking cigarettes may interfere with the effectiveness of acetaminophen. Smokers may need to take higher doses of the medicine, but should not take more than the recommended daily dosage unless told by a physician to do so.
Many drugs can interact with one another. Consult a physician or pharmacist before combining acetaminophen with any other medicine. Do not use two different acetaminophen-containing products at the same time.
Acetaminophen interferes with the results of some medical tests. Before having medical tests done, check to see whether taking acetaminophen will affect the results. Avoiding the drug for a few days before the tests may be necessary.
Side effects
Acetaminophen causes few side effects. The most common one is lightheadedness. Some people may experience trembling and pain in the side or the lower back. Allergic reactions do occur in some people, but they are rare. Anyone who develops symptoms such as a rash, swelling, or difficulty breathing after taking acetaminophen should stop taking the drug and get immediate medical attention. Other rare side effects include yellow skin or eyes, unusual bleeding or bruising, weakness, fatigue, bloody or black stools, bloody or cloudy urine, and a sudden decrease in the amount of urine.
Overdoses of acetaminophen may cause nausea, vomiting, sweating, and exhaustion. Very large overdoses can cause liver damage. In case of an overdose, get immediate medical attention.
Interactions
Acetaminophen may interact with a variety of other medicines. When this happens, the effects of one or both of the drugs may change or the risk of side effects may be greater. Among the drugs that may interact with acetaminophen are alcohol, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as Motrin, oral contraceptives, the antiseizure drug phenytoin (Dilantin), the blood-thinning drug warfarin (Coumadin), the cholesterol-lowering drug cholestyramine (Questran), the antibiotic Isoniazid, and zidovudine (Retrovir, AZT). Check with a physician or pharmacist before combining acetaminophen with any other prescription or nonprescription (over-the-counter) medicine.
Key Terms
- Arthritis
- Inflammation of the joints. The condition causes pain and swelling.
- Fatigue
- Physical or mental weariness.
- Inflammation
- A response to irritation, infection, or injury, resulting in pain, redness, and swelling.
Further Reading
Gale Encyclopedia of Medicine. Gale Research, 1999.