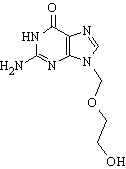
Acyclovir
Aciclovir (INN) or acyclovir (USAN), marketed as Zovirax®, is one of the main antiviral drugs. Its discovery has been seen as the start of a new era in antiviral therapy, as it is extremely selective and low in cytotoxicity. However, it has a very narrow spectrum, only effective against certain viruses such as HSV-1, HSV-2, and VZV, with limited effectiveness against active EBV, and has hardly any effect against human cytomegalovirus (CMV). It is about 10 times more potent against HSV than VZV. more...
It does not eradicate latent herpes, and does not work very well against genital herpes in women. Aciclovir is rather different from other nucleoside analogues, for it contains only a partial nucleoside structure as the sugar ring is replaced by an open-chain structure.
Mode of action
Aciclovir is converted into monophosphate form only by viral thymidine kinase, which is far more effective (3000 times) in phosphorylation than cellular thymidine kinase. Subsequently, the monophosphate form is further phosphorylated into the active triphosphate form, aciclo-GTP, by cellular kinases. Aciclo-GTP is a very potent inhibitor of viral DNA polymerase; it has approximately 100 times higher affinity to viral than cellular polymerase. Its monophosphate form also incorporates into the viral DNA, resulting in chain termination. It has also been shown that the viral enzymes cannot remove acyclo-GMP from the chain, which results in inhibition of further activity of DNA polymerase. Acyclo-GTP is fairly rapidly metabolised within the cell, possibly by cellular phosphatases.
Pharmacokinetics
Aciclovir suffers from low water solubility, and also from poor oral absorption, which is only 20%. Orally administered the peak plasma concentration will be reached in 1-2 hours. If large doses are required, aciclovir must be administered intravenously. Aciclovir has a high distribution rate, only 30 % is protein-bound in plasma. The half-life of aciclovir is approximately 3 hours. Aciclovir can also be given topically for treatment of herpes infections of mucous membrane and skin, such as genital herpes or recurrent herpes labialis (cold sore). Prophylactic administration is possible, and is often used for patients who are under immunosuppressant drugs or radiotherapy or for those who are suffering from recurrent genital infection herpes simplex.
Metabolism
The excretion of aciclovir takes place via the renal system, partly by glomerular filtration and partly by tubular secretion. Renal problems have been reported when given in large, fast doses intravenously, due to the crystallisation of aciclovir in the kidneys.
Side effects
Since aciclovir can be incorporated also into the cellular DNA, it is a chromosome mutagen, therefore, its use should be avoided during pregnancy. However it has not been shown to cause any teratogenic nor carcinogenic effects. The acute toxicity (LD50) of aciclovir when given orally is greater than 1mg/kg, due to the low absorption rate from the gastrointestinal tract. Single cases have been reported, where extremely high (up to 80mg/kg) doses have been accidentally given intravenously without causing any side effects. The most common adverse effects are local irritation at the site of injection, headache when given orally, and a stinging and burning sensation when administered topically. The resistance towards aciclovir evolves rather rapidly, although this has not much hindered its clinical use. Resistant forms are most likely viruses that have a mutation in their thymidine kinase or DNA polymerase.
Read more at Wikipedia.org