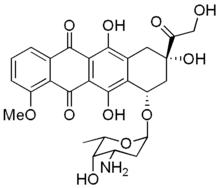
Adriamycin
Doxorubicin or adriamycin is a DNA-interacting drug widely used in chemotherapy. It is an anthracycline and structurely closely related to daunomycin, and also intercalates DNA. It is commonly used in the treatment of uterine cancer and ovarian cancer, as well as some other cancers. more...
Doxil® is a liposome-encapsulated dosage form of doxorubicin made by Johnson & Johnson. Its main benefits are a reduction in cardiotoxicity. It follows the similar preparation of daunorubicin in a liposomal carrier.
Mechanism of Action
Doxorubicin acts by binding to DNA where it can inhibit the progression of the enzyme topoisomerase II, which unwinds DNA for transcription. Doxorubicin stabilises the topoisomerase II complex after it has broken the DNA chain for replication, preventing the DNA double helix from being resealed and thereby stopping the process of replication.
Side Effects
Acute side-effects of doxorubicin are nausea, vomiting, decrease in white blood cells and hair loss. When the cumulative dose of doxorubicin reaches 450mg/m2, the risk of congestive heart failure dramatically increases.
Clinical Use
Doxorubicin is a commonly used to treat Hodgkins disease, breast cancer, lung cancer, soft tissue sarcoma, Kahlers disease.
Read more at Wikipedia.org