Aleve
Naproxen (trade names: Aleve, Anaprox, Naprogesic, Naprosyn, Naprelan) is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) commonly used for the reduction of mild to moderate pain, fever, inflammation and stiffness caused by conditions such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, gout, ankylosing spondylitis, injury, menstrual cramps, tendinitis, bursitis, and the treatment of primary dysmenorrhea. It works by reducing hormones that cause inflammation and pain in the body. more...
Although naproxen typically requires a higher dosage than other NSAIDs — a minimal dose is about 200 mg — it binds very well to albumin and thus achieves a longer half-life in the blood than other drugs, lasting up to 12 hours per dose.
Naproxen is also available as a sodium salt, naproxen sodium, which is more rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract.
Naproxen was first sold as the prescription drug Naprosyn in 1976; naproxen sodium was first sold under the trade name Anaprox in 1980. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved naproxen sodium's use as an over-the-counter drug in 1991 , and it is sold in the United States as Aleve. Naproxen is still a prescription drug in much of the world, including Canada.
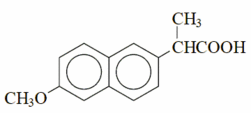
Structure and details
Naproxen is a member of the arylacetic acid family of NSAIDs. It is an odorless, white to off-white crystalline substance with a molecular weight of 230.2628. It is lipid-soluble, practically insoluble in water with a low pH (below pH 4), while freely soluble in water at 6 pH and above. Naproxen has a melting point of 153 °C.
Side effects and warnings
Like other NSAIDs, naproxen is capable of producing disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract. Taking the medication with food may help to alleviate this most commonly reported side-effect.
Also like other NSAIDs, naproxen can inhibit the excretion of sodium and lithium. Extreme care must be taken by those who use this drug along with lithium supplements.
Naproxen is also not recommended for use with NSAIDs of the salicylate family (drugs may reduce each other's effects), nor with anticoagulants (may increase risk of bleeding).
In December 2004, the FDA issued a press release following the decision by the National Institutes of Health to halt a five-year study, called the Alzheimer's Disease Anti-Inflammatory Prevention Trial. That study aimed to test both Aleve and Celebrex as preventatives for Alzheimer's disease. Preliminary information from the study showed naproxen elevated the risk of heart attack and stroke by 50%. The FDA advised patients taking over-the-counter naproxen products to:
- carefully follow the instructions on the label,
- avoid exceeding the recommended doses for naproxen (220 milligrams twice daily), and
- take naproxen for no longer than ten days unless a physician directs otherwise.
Read more at Wikipedia.org