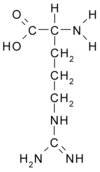
Q: I'm a little confused about the difference between arginine and nitric oxide (NO) products. What does each do for bodybuilders?
A: They're essentially the same thing. Most NO products contain arginine. When it comes to comparing these types of products, they are equivalent: Both arginine and NO products enhance biological functions that are beneficial for bodybuilders wanting to make gains.
Richard Kreider, PhD, FACSM, is professor and chair of the Exercise & Sport Nutrition Laboratory at Baylor University (Waco, Texas).
"Arginine is an amino acid while nitric oxide is a gas that's produced from arginine," he says. "Whether you take arginine or an NO product, the nitric oxide works as a hemodilator that relaxes smooth muscle in your arteries." This not only reduces blood pressure but also increases blood flow to your muscles by dilating your blood vessels. The advantage of increased blood flow is that nutrients, oxygen and hormones will be more readily delivered to your muscles.
The increase in blood flow delivers a noticeable muscle "pump," Kreider points out. While little research has been conducted to scientifically assess this effect on resistance-trained athletes, anecdotal reports strongly support arginine's--and thus NO's--effect on an enhanced pump while weight training.
In addition to these direct effects, arginine supplementation provides many other health benefits for select groups. "Studies have shown that arginine/NO supplementation will not only increase local blood flow and reduce blood pressure, but it may also influence cell growth, reduce catabolism during surgical stays and improve sexual function in men," Kreider says. NO helps to overcome erectile dysfunction through improved blood flow.
Kreider has conducted studies on arginine alpha-ketoglutarate (AKG, a modified version of L-arginine) supplementation. "The research is promising for resistance-trained athletes," he says. "But additional research is needed to better evaluate the role of L-arginine or AKG supplementation on training adaptations before definitive conclusions can be drawn."
NPC bodybuilder Erick Fromm competes as a super-heavyweight.
"For me, arginine is a mainstay. When you first take an NO product, you can't believe how much more of a pump you feel when you're weight training," he says. "It's amazing. You feel it the first time you take it. You can see and feel the increased pump in your target muscles, and you have more muscular endurance."
Erick recommends taking arginine or NO products in cycles. "I use it as a motivator. When I first start to take it, I seem to get more benefit than when I've been taking it for several weeks." He suggests taking NO products for six weeks on, then four weeks off, although many experts see no need to cycle arginine.
For best results, look for an NO product that contains at least 3 grams of AKG or, if your product has L-arginine, take a dosage of 2-5 grams. Arginine or NO products in this dosage range should be taken 2-3 times a day on an empty stomach--the first in the morning, the second 30-60 minutes before your workout and the third later in the day. For added benefits, check labels to see if your product includes forskolin, cirtulline or inulin to potentially enhance the effects of NO.
COPYRIGHT 2005 Weider Publications
COPYRIGHT 2005 Gale Group