Definition
Azacitidine, is an antineoplastic (antitumor) agent that acts by interfering with the growth of cells.
Purpose
Azacitidine is a chemotherapy drug used primarily to treat adults and children with acute myelocytic leukemia that has not responded to traditional therapy. It is also used to treat myelodysplastic syndrome. There is limited data that azacitidine may be useful for chronic myelogenous leukemia, sickle cell anemia, and cancers that have spread to other organs in the body. It should also be noted that azacitidine does not appear on the FDA's approved drug list. Currently, azacitidine is prescribed only as an experimental drug.
Description
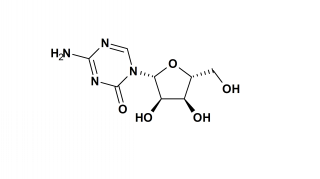
DNA can be thought of as the blueprint for the cell, and RNA as the messenger to carry out the instructions of the DNA. RNA, or ribonucleic acid, is a close relative of DNA, deoxyribonucleic acid. Both are made up of four different bases, adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine. Azacitidine pretends to be cytosine, and is incorporated into the RNA and DNA of cells, inhibiting them from carrying out their normal functions and causing cell death.
Recommended dosage
The dose of azacitidine depends on the reason it is being administered and whether any other drugs are involved in treatment. The usual dose for azacitidine is 50 to 200 mg per square meter of body surface area per day for five to 10 days. This is repeated at two to three week intervals. Azacitidine is administered either through the vein or injected under the skin. It may be injected under the skin at a dose of 75 mg per square meter of body surface area per day for seven days, to be repeated every 4 weeks.
Precautions
Pregnant women should not take this drug, and should be aware that this drug has been shown to cause death or abnormality in the fetuses of laboratory animals. Women who might become pregnant while taking this medication should take steps to ensure that they do not. Nursing mothers should discontinue nursing while taking this medication. All patients should have this drug administered by a health care professional and their progress regularly monitored.
Side effects
The most common side effect of azacitidine is the decreased production of white blood cells, which are important in fighting infections, and platelets, which are important in preventing bleeding. Nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea are also very common with this drug.
Other side effects include fever, general muscle pain, weakness, and lethargy. Decreased liver function, low blood pressure, and changes in kidney function have also been reported with azacitidine. Also, injections of the drug under the skin can cause redness, swelling, or mild pain.
Interactions
Azacitidine has no known interactions with other drugs. However, prior to initiating any over-the-counter, herbal, or new medications, patients should consult their physician, nurse, or pharmacist to prevent possible drug interactions.
KEY TERMS
- Gene
- A functional unit of DNA.