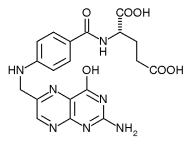
Folic acid
Folic acid and folate (the anion form) are forms of a water-soluble B vitamin. These occur naturally in food and can also be taken as supplements. Folate gets its name from the Latin word folium, leaf. more...
History
A key observation of researcher Lucy Wills nearly 70 years ago led to the identification of folate as the nutrient needed to prevent the anemia of pregnancy. Dr. Wills demonstrated that the anemia could be corrected by a yeast extract. Folate was identified as the corrective substance in yeast extract in the late 1930s and was extracted from spinach leaves in 1941.
Biological roles
Folate is necessary for the production and maintenance of new cells. This is especially important during periods of rapid cell division and growth such as infancy and pregnancy. Folate is needed to replicate DNA and synthesize RNA. It also helps prevent changes to DNA that may lead to cancer. Both adults and children need folate to make normal red blood cells and prevent anemia.
Biochemistry
In the form of a series of tetrahydrofolate compounds, folate derivatives are coenzymes in a number of single carbon transfer reactions biochemically, and also is involved in the synthesis of dTMP (2'-deoxythymidine-5'-phosphate) from dUMP (2'-deoxyuridine-5'-phosphate).
The pathway in the formation of tetrahydrofolate (FH4) is the reduction of folate (F) to dihydrofolate (FH2) by folate reductase, and then the subsequent reduction of dihydrofolate to tetrahydrofolate (FH4) by dihydrofolate reductase.
Methylene tetrahydrofolate (CH2FH4) is formed from tetrahydrofolate by the addition of methylene groups from one of three carbon donors: formaldehyde, serine, or glycine. Methyl tetrahydrofolate (CH3–FH4) can be made from methylene tetrahydrofolate by reduction of the methylene group, and formyl tetrahydrofolate (CHO-FH4, folinic acid) is made by oxidation of the methylene tetrahydrofolate.
In other words:
F → FH2 → FH4 → CH2=FH4 → 1-carbon chemistry
A number of drugs interfere with the biosynthesis of folic acid and tetrahydrofolate. Among them are the dihydrofolate reductase inhibitors (such as trimethoprim and pyrimethamine, the sulfonamides (competitive inhibitors of para-aminobenzoic acid in the reactions of dihydropteroate synthetase) and the anticancer drug methotrexate (inhibits both folate reductase and dihydrofolate reductase).
Recommended Dietary Allowance for folate
The Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) is the average daily dietary intake level that is sufficient to meet the nutrient requirements of nearly all (97 to 98 percent) healthy individuals in each life-stage and gender group. The 1998 RDAs for folate are expressed in a term called the Dietary Folate Equivalent (DFE). This was developed to help account for the differences in absorption of naturally-occurring dietary folate and the more bioavailable synthetic folic acid. The 1998 RDAs for folate expressed in micrograms (µg) of DFE for adults are:
Read more at Wikipedia.org