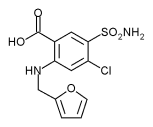
Furosemide
Furosemide (INN) or frusemide (former BAN) is a loop diuretic used in the treatment of congestive heart failure and edema. It is most commonly marketed by Aventis Pharma under the brand name Lasix. It has also been used to prevent thoroughbred race horses from bleeding through the nose during races. more...
Along with some other diuretics, furosemide is also included on the World Anti-Doping Agency's banned drug list due to its alleged use as a masking agent for other drugs.
Mechanism of action
Like other loop diuretics, furosemide acts by inhibiting the Na/K/Cl cotransporter in the ascending loop of Henle. It also has inhibitory activity on carbonic anhydrase.
Clinical use in humans
Furosemide, as a loop diuretic, is principally used in the following indications (Aventis, 1998):
- Edema associated with heart failure, hepatic cirrhosis, renal impairment, nephrotic syndrome
- Hypertension
- Adjunct in cerebral/pulmonary oedema where rapid diuresis is required (IV injection)
It is also sometimes used in the management of severe hypercalcemia in combination with adequate rehydration (Rossi, 2004).
It is considered ototoxic. (PMID 15311369)
Use in horses
Apparently, sometime in the early 1970s, furosemide's ability to prevent or at least greatly reduce the incidence of bleeding by horses during races was discovered accidentally. Pursuant to the racing rules of most states, horses that bleed from the nostrils three times are permanently barred from racing (for their own protection). Clinical trials followed, and by decade's end, racing commissions in some states began legalizing its use on race horses. On September 1, 1995, New York became the last state in the United States to approve such use, after years of refusing to consider doing so. Some states allow its use for all racehorses; some allow it only for confirmed "bleeders." Its use for this purpose is still prohibited in many other countries, however.
Brand names
Some of the brand names under which furosemide is marketed include: Aisemide®; Beronald®; Desdemin®; Discoid®; Diural®; Diurapid®; Dryptal®; Durafurid®; Errolon®; Eutensin®; Frusetic®; Frusid®; Fulsix®; Fuluvamide®; Furesis®; Furo-Puren®; Furosedon®; Hydro-rapid®; Impugan®; Katlex®; Lasilix®; Lasix®; Lowpston®; Macasirool®; Mirfat®; Nicorol®; Odemase®; Oedemex®; Profemin®; Rosemide®; Rusyde®; Trofurit®; Urex®
Read more at Wikipedia.org