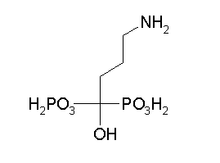
Fosamax
Alendronate (Fosamax®, Merck) is a bisphosphonate drug used for osteoporosis and several other bone diseases. It is marketed alone as well as in combination with vitamin D (2,800 U, under the name Fosavance). more...
Pharmakokinetics
The systemic bioavailability after oral dosing is only 0.6 % as well in women and in men (fasting state). Intake together with meals and certain drinks (coffee, orange juice) further reduces the bioavailability. Soft tissues and bones are fastly reached by about 50%. After resorption in the bone alendronate has an estimated terminal halflife of 10 years; the remainder is excreted unchanged by the kidneys.
Pharmacology
Alendronate blocks osteoblast-mediated bone-resorption. It is chemically related to etidronate and the N-containing bisphosphonates such as pamidronate, which with it shares the same mode of action. Its inhibition of bone-resorption is dose-dependent and 100 to 1,000 times stronger than the equimolar effect of etidronate. Theoretically, alendronate may also inhibit bone-mineralization but this effect is 6,000 times weaker than the inhibition of bone-resorption. Under therapy normal bone tissue develops and alendronate is deposited in the bone-matrix in pharmacologically inactive form. For optimal action enough calcium and vitamin D are needed in the body. Hypocalcemia should therefore be corrected before starting therapy.
Uses
- Prophylaxis and treatment of female osteoporosis
- Treatment of male osteoporosis
- Prevention and treatment of corticosteroid-associated osteoporosis together with supplements of calcium and vitamin D
- Paget's disease
Contraindications and precautions
- Acute inflammations of the gastrointestinal tract (esophagitis, gastritis, ulcerations)
- Clinically manifest osteomalacia
- Certain malformations and malfunctions of the esophagus (strictures, achalasia)
- Unability to stand, walk, or sit for 30 minutes after oral administration
- Renal impairment with a creatinine clearance below 30ml/min
- Hypersensitivity to alendronate or another ingredient
- Hypocalcemia
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding
- Patients below 18 yrs. of age, because no clinical data exists
Side-effects
- GI tract: most prominent are harmless side effects such as mild nausea, dyspepsia, abdominal cramps, flatulence, diarrhea, or obstipation. A severe side effect is an ulceration of the esophagus caused by alendronate, which may require hospitalization and intensive treatment. Gastric and duodenal ulceration.
- General: infrequent cases of skin rash, rarely manifesting as Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis, eye problems (uveitis, scleritis) and generalized muscle, joint, and bone pain (rarely severe) have been seen. In laboratory tests decreased calcium and phosphate values may be obtained but reflect action of the drug and are harmless.
- Osteonecrosis of the jaw, a recognised but rare side-effect of bisphosphonates
Read more at Wikipedia.org