Measurin
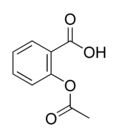
Aspirin or acetylsalicylic acid is a drug in the family of salicylates, often used as an analgesic (against minor pains and aches), antipyretic (against fever), and anti-inflammatory. It has also an anticoagulant (blood-thinning) effect and is used in long-term low-doses to prevent heart attacks. more...
Low-dose long-term aspirin irreversibly blocks formation of thromboxane A2 in platelets, producing an inhibitory effect on platelet aggregation, and this blood-thinning property makes it useful for reducing the incidence of heart attacks. Aspirin produced for this purpose often comes in 75 or 81 mg dispersible tablets and is sometimes called "Junior aspirin." High doses of aspirin are also given immediately after an acute heart attack. These doses may also inhibit the synthesis of prothrombin and may therefore produce a second and different anticoagulant effect.
Several hundred fatal overdoses of aspirin occur annually, but the vast majority of its uses are beneficial. Its primary undesirable side effects, especially in stronger doses, are gastrointestinal distress (including ulcers and stomach bleeding) and tinnitus. Another side effect, due to its anticoagulant properties, is increased bleeding in menstruating women. Because there appears to be a connection between aspirin and Reye's syndrome, aspirin is no longer used to control flu-like symptoms in minors.
Aspirin was the first discovered member of the class of drugs known as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), not all of which are salicylates, though they all have similar effects and a similar action mechanism.
ASPIRIN
The brand name Aspirin was coined by the Bayer company of Germany. In some countries the name is used as a generic term for the drug rather than the manufacturer's trademark. In countries in which Aspirin remains a trademark, the initialism ASA is used as a generic term (ASS in German-language countries, for Acetylsalicylsäure; AAS in Spanish- and Portuguese-language countries, for ácido acetilsalicílico).
The name "aspirin" is composed of a- (from the acetyl group) -spir- (from the spiraea flower) and -in (a common ending for drugs at the time). Bayer registered it as a trademark on March 6, 1899.
However, the German company lost the right to use the trademark in many countries as the Allies seized and resold its foreign assets after World War I. The right to use "Aspirin" in the United States (along with all other Bayer trademarks) was purchased from the U.S. government by Sterling Drug, Inc. in 1918. Even before the patent for the drug expired in 1917, Bayer had been unable to stop competitors from copying the formula and using the name elsewhere, and so, with a flooded market, the public was unable to recognize "Aspirin" as coming from only one manufacturer. Sterling was subsequently unable to prevent "Aspirin" from being ruled a genericized trademark in a U.S. federal court in 1921. Sterling was ultimately acquired by Bayer in 1994, but this did not restore the U.S. trademark. Other countries (such as Canada) still consider "Aspirin" a protected trademark.
Read more at Wikipedia.org