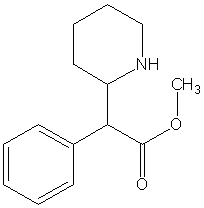
Methylphenidate
Methylphenidate (MPH) is an amphetamine-like prescription stimulant commonly used to treat Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) in children and adults. It is also one of the primary drugs used to treat symptoms of traumatic brain injury and the daytime drowsiness symptoms of narcolepsy and chronic fatigue syndrome. Brand names of drugs that contain methylphenidate include Ritalin®, Concerta® (a timed-release capsule), Metadate®, Methylin® and Rubifen®. more...
Focalin® is a preparation containing only dextro-methylphenidate, rather than the usual racemic dextro- and laevo-methylphenidate mixture of other formulations.
History
Methylphenidate was patented in 1954 by the Ciba Pharmaceutical Company (a precursor to Novartis) and was initially prescribed as a treatment for depression, chronic fatigue, and narcolepsy, among other ailments. Beginning in the 1960s, it was used to treat children with ADHD, known at the time as hyperactivity or minimal brain dysfunction (MBD). Today methylphenidate is the medication most commonly prescribed to treat ADHD around the world. According to most estimates, more than 75 percent of methylphenidate prescriptions are written for children, with boys being about four times as likely to take methylphenidate as girls. Production and prescription of methylphenidate rose significantly in the 1990s, especially in the United States, as the ADHD diagnosis came to be better understood and more generally accepted within the medical and mental health communities.
Most brand-name Ritalin is produced in the United States, although methylphenidate is also produced in Mexico and Argentina by respective contract pharmaceutical manufacturers and is marketed under the brand name "Ritalin" for Novartis. In the United States, various generic forms of methylphenidate are also produced by several pharmaceutical companies (such as Methylin, etc.), and Ritalin is also sold in the United Kingdom, Germany, and other European countries (although in much lower volumes than the United States). Another medicine is Concerta. This was approved around the date of April 2000.
Effects
Methylphenidate is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant. It has a "calming" effect on many children who have ADHD, reducing impulsive behavior and the tendency to "act out", and helps them concentrate on schoolwork and other tasks. Adults who have ADHD often find that MPH increases their ability to focus on tasks and organize their lives.
The means by which methylphenidate helps people with ADHD are not well understood. Some researchers have theorized that ADHD is caused by a dopamine imbalance in the brains of those affected. MPH is a dopamine reuptake inhibitor, which means that it increases the level of the dopamine neurotransmitter in the brain by partially blocking the transporters that remove it from the synapses.
In the United States, methylphenidate is classified as a Schedule II controlled substance, the designation used for substances that have a recognized medical value but which have a high potential for abuse. Internationally, methylphenidate is a Schedule II drug under the Convention on Psychotropic Substances. Some people abuse MPH by crushing the tablets and snorting them, the "high" resulting from the higher equivalent dose being absorbed rapidly into the bloodstream. The effect of Ritalin is similar to that of cocaine or amphetamine and such abuse can lead to addiction. When taken orally in prescribed doses, MPH is less addictive and may not produce a "high". After taking the drug or resuming it after going a month or more without it, the effects of dependence will tend to level off after a week, and again, after a month.
Read more at Wikipedia.org