Carnitine
Carnitine, also known as L-carnitine is an amino acid responsible for transport of fatty acids into a cell's mitochondria. It is often sold as a nutritional supplement. more...
Like all other proteinogenic amino acids natural carnitine is the L-stereoisomer. It can be synthesised within the body from the amino acids lysine or methionine. Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) is essential to the synthesis of carnitine. It has been speculated that during growth or pregnancy the requirement of carnitine could exceed its natural production.
Role in fatty acid metabolism
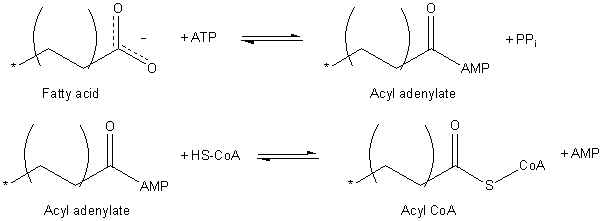
Fatty acids must be activated before they can be carried into the mitochondria, where fatty acid oxidation occurs. This process occurs in two steps:
The formula for the above is:
RCOO- + CoA + ATP + H2O → RCO-CoA + AMP + PPi + 2H+
This reaction is reversible and its equilibrium lies near 1. However, pyrophosphate is hydrolized by a pyrophosphatase, which drives the reaction forward, and to completion.
Once activated, the acyl CoA is transported into the mitochondrial matrix. This occurs via a series of similar steps:
- Acyl CoA is conjugated to carnitine by carnitine acyltransferase I located on the outer mitochondrial membrane
- Acyl carnitine is shuttled inside by a translocase
- Acyl carnitine is converted to acyl CoA by carnitine acyltransferase II located on the inner mitochondrial membrane
It is important to note that carnitine acyltransferase I undergoes allosteric inhibition as a result of malonyl CoA, an intermediate in fatty acid biosynthesis.
Natural sources
The best source of natural carnitine is in red meat and dairy products. Other natural sources of Carnitine include nuts and seeds (e.g pumpkin, sunflower, sesame), legumes or pulses (beans, peas, lentils, peanuts), vegetables (artichokes, asparagus, beet greens, broccoli, brussels sprouts, collard greens, garlic, mustard greens, okra, parsley), fruits (apricots, bananas), cereals (buckwheat, corn, millet, oatmeal, rice bran, rye, whole wheat, wheat bran, wheat germ) and other 'health' foods (bee pollen, brewer's yeast, carob, kale).
Acetyl-L-carnitine
section references:
Acetyl-L-carnitine or ALCAR, is an acetylated form of L-carnitine. ALCAR is far superior to normal L-carnitine in terms of bioavailability in that it is absorbed by the gastrointestinal tract, enters cells and crosses the blood-brain barrier more readily than unacetylated carnitine.
ALCAR has a broad range of uses including combination with alpha lipoic acid to comprise a patented formulation that has been evidenced to "rejuvenate" the mitochondria of aging mice in studies conducted by Bruce Ames and others. Accordingly, acetyl-L-carnitine has potential as a life extension supplement probably capable of improving the quality and possibily also extending the average life-span of humans. Other attributed uses for ALCAR include using it as a treatment for depression (250 mg per day for several weeks) and for clearing plaque/fatty deposits out of the veins and arteries.
Read more at Wikipedia.org