Cotrim
Co-trimoxazole (abbreviated SXT) is a bacteriostatic antibiotic combination of trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole, in the ratio of 1 to 5, used in the treatment of a variety of bacterial infections. The name co-trimoxazole is the International Nonproprietary Name, and has been marketed worldwide under many brand names (GlaxoSmithKline under Septrin®, Hoffmann-La Roche as Bactrim®, and by many other generic pharmaceutical manufacturers). more...
Synergistic action
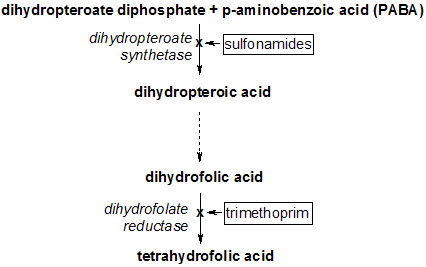
Co-trimoxazole exhibits a synergistic antibacterial effect when compared to each of its components administered singly. This is because trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole inhibit successive steps in the folate synthesis pathway (see diagram below).
Sulfamethoxazole acts as a false-substrate inhibitor of dihydropteroate reductase. Sulfonamides such as sulfamethoxazole are analogues of p-aminobenzoic acid (PABA) and are competitive inhibitors of the enzyme; inhibiting the production of dihydropteroic acid.
Trimethoprim acts by interfering with the action of bacterial dihydrofolate reductase, inhibiting synthesis of tetrahydrofolic acid.
Folic acid is an essential precursor in the de novo synthesis of the DNA nucleosides thymidine and uridine. Bacteria are unable to take up folic acid from the environment (i.e. the infection host) thus are dependent on their own de novo synthesis - inhibition of the enzyme starves the bacteria of two bases necessary for DNA replication and transcription.
Clinical indications
Co-trimoxazole is more effective than either of its components individually in treating bacterial infections. However the degree of benefit for the additonal of the Sulfonamide, was in most cases marginal, but reponsible for its high association will allergic responses (see below). Its widespread use has been restricted in many countries to very specific circumstances where its improved efficacy is demonstrated. It may be effective in a variety of upper and lower respiratory tract infections, renal and urinary tract infections, gastrointestinal tract infections, skin and wound infections, septicaemias and other infections caused by sensitive organisms.
Specific indications for its use include: (Rossi, 2004)
- treatment and prophylaxis of pneumonia caused by Pneumocystis jiroveci (P. carinii)
- infections caused by Listeria monocytogenes, Nocardia spp., Stenotrophomonas maltophilia (Zanthomonas maltophilia)
- melioidosis
- shigellosis
- traveller's diarrhoea
- prophylaxis of cerebral toxoplasmosis in HIV patients
- Whipple's disease
Safety
There has been some concern about its use, however, since it has been associated with both frequent mild allergic reactions and rare but serious adverse effects including Stevens-Johnson syndrome, myelosuppression, agranulocytosis, as well as severe liver damage (cholostatic hepatosis, hepatitis, liver necrosis, fulminant liver failure) and renal impairment up to acute renal failure and anuria. These side-effects are seen especially in the elderly and may be fatal. (Joint Formulary Committee, 2004)
Read more at Wikipedia.org