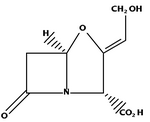
Clavulanic acid
Clavulanic acid is in a class of medications called the beta-lactamase inhibitors. It works by preventing bacteria that release beta-lactamases from destroying beta-lactam antibiotics. In the form of Potassium Clavulanate it is combined with Amoxicillin (to form Co-amoxiclav) or Ticarcillin (to form Timentin®) to treat otherwise resistant bacterial infections, including infections of the ears, lungs, sinus, skin, and urinary tract. more...
Clavulanic acid is produced by cultures of Streptomyces Clavuligerus.
Mechanism of action
Clavulanic acid, like the beta-lactam antibiotics, has a β-lactam ring. It has no intrinsic antimicrobial effect, yet it can competitively inhibit β-lactamases. β-lactamases are much more inclined to bind to clavulanic acid than to the beta-lactam antibiotic. In binding β-lactamases to clavulanic acid, a long-lasting inactive molecule is produced. In this way, bacterial β-lactamases miss their target, and the intact beta-lactam antibiotic can reach the bacterial cell wall. However, some bacteria have acquired genes to produce enzymes which circumvent the action of beta-lactamase inhibitors, dramatically reducing the efficacy of these agents.
Adverse effects
Use of clavulanates with penicillins has been associated with the development of cholestatic jaundice and hepatitis, and as such the UK Committee on Safety of Medicines recommends that treatments such as co-amoxiclav (Amoxicillin and Clavulanic acid) should be reserved for bacterial infections likely to be caused by amoxicillin-resistant β-lactamase-producing strains, and that treatment should not normally exceed 14 days.
Read more at Wikipedia.org