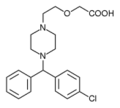
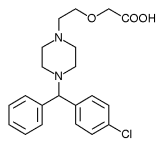
This case report describes the use of up to 50 mg of cetirizine in the treatment of chronic idiopathic urticaria. A 40-year old man presented with a 4-week history of generalized urticaria. The onset of symptoms were not associated temporally with food, exercise, cold exposure, pressure, sun exposure, vibrations, medications, or any precipitating factors. Laboratory workup failed to reveal any evidence of cryoglobulins, ANA antibodies, antithyroid antibodies, hepatitis antibodies, or HIV. The patient was initially started on cetirizine 10 mg per day without improvement. His dose was increased to 20 mg, again with no improvement. Ranitidine was added, and the dose of cetirizine was increased to 30 mg per day, resulting in some improvement. The patient finally achieved relief with Cetirizine 40 mg per day, with the use of an extra 10 mg for breakthrough episodes of wheals. He denied any complaints of sedation, even at five times the recommended adult dose.
Nordness M et al. High Dose Cetirizine: A Case Report. Cutis 2003; 71:296.
COPYRIGHT 2003 Journal of Drugs in Dermatology
COPYRIGHT 2003 Gale Group